- 30/05/2023
- Posted by: Thamizharasu Gopalsamy
- Categories: Business Growth, Management
Introduction:
In an increasingly competitive business landscape, strategic planning is more crucial than ever. One of the key tools used by businesses worldwide for this purpose is the Ansoff Matrix. Developed by H. Igor Ansoff, the ‘father of strategic management’, the matrix provides a blueprint for organizations to chart their growth strategies. This comprehensive guide dives deep into the concept of the Ansoff Matrix, its core components, real-world examples, and how to successfully incorporate it into your strategic planning.
1. The Basics of Ansoff Matrix: A Comprehensive Guide
What is the Ansoff Matrix?
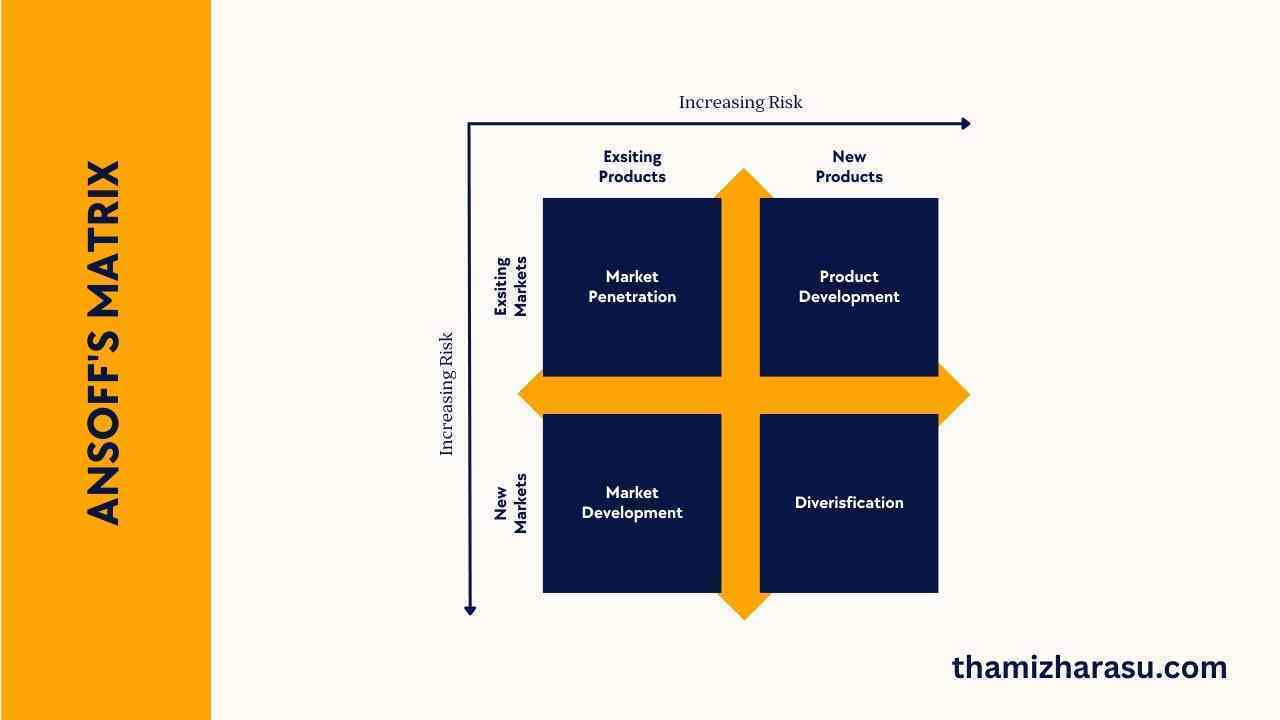
Start by introducing the Ansoff Matrix, also known as the Product/Market Expansion Grid. It’s a strategic planning tool developed by H. Igor Ansoff in 1957 to help businesses chart out strategies for growth.
Purpose and Benefits of the Ansoff Matrix
Discuss why the Ansoff Matrix is essential. Its main purpose is to provide a framework for organizations to identify growth opportunities by assessing potential risks and rewards in line with the company’s capabilities and resources. Furthermore, it helps businesses explore strategies regarding existing and new markets and products.
Components of the Ansoff Matrix
The Ansoff Matrix consists of four quadrants, each representing a specific growth strategy. The four are Market Penetration, Market Development, Product Development, and Diversification. Briefly introduce these strategies:
Market Penetration: Growing by selling more of existing products to existing customers.
Market Development: Growth is achieved by selling existing products to new markets.
Product Development: Involves creating new products for existing customers.
Diversification: It is about creating new products for new markets.
Understanding the Risk Factor
In the Ansoff Matrix, risk tends to increase from Market Penetration to Diversification. Explain this aspect and how it helps businesses in their decision-making process.
2. Understanding the Four Quadrants of the Ansoff Matrix
Market Penetration Strategy
Begin by explaining that this strategy involves selling more of the existing products to the existing customers. Companies can achieve this by promoting their products, introducing loyalty schemes, or finding creative ways to increase usage. Give an example, such as a coffee shop offering loyalty cards to encourage repeat visits from existing customers.
Market Development Strategy
This strategy involves selling existing products to new markets. This can be achieved through geographic expansion, targeting new demographic segments, or finding new uses for the product. An example could be a clothing brand originally aimed at young adults, which decides to launch a new line for teenagers.
Product Development Strategy
Product development refers to creating new products for the existing market. Companies could achieve this by investing in research and development, innovation, or improving the current products based on customer feedback. A tech company releasing a new version of its existing software with added features is a good example of this strategy.
Diversification Strategy
Diversification is the most risky strategy as it involves creating new products for new markets. There are two types of diversification – related and unrelated. Related diversification is when a company stays within an industry it is familiar with; unrelated diversification involves moving into an entirely new industry. An example of diversification is when a book publishing company decides to develop an e-reader device and sell it to a new market segment.
Remember, each strategy carries a different level of risk and potential return, and companies often choose a mix of these strategies based on their unique circumstances and resources.
3. Understanding Product Development
Start by defining product development within the context of the Ansoff Matrix. It is a growth strategy that involves creating new or improved products for the existing market. This strategy can be used when a company identifies an opportunity to innovate its products to meet the evolving needs of its current customers.
Steps in Product Development Strategy
Discuss the steps involved in implementing a product development strategy:
1. Idea Generation: Gathering innovative ideas for a new product.
2. Idea Screening: Filtering the ideas to select the most viable one.
3. Concept Development and Testing: Creating and evaluating product design ideas.
4. Marketing Strategy and Development: Developing a strategy to launch and promote the product.
5. Product Development and Testing: Actual development and testing of the product.
6. Commercialization: Launching the product in the market.
Benefits of Product Development Strategy
Highlight the benefits of this strategy, such as meeting customer demands, staying ahead in the market, gaining a competitive edge, and improving market share.
Challenges and Risks of Product Development Strategy
Also, mention the challenges and risks involved, like high research and development costs, market acceptance of the new product, and potential failure of the product.
Examples of Product Development Strategy
End with a few examples of successful product development strategies. For instance, Apple is known for continuously innovating and improving its products like iPhones and Macbooks to cater to the evolving needs of its existing customers.
By providing an in-depth understanding of product development as per the Ansoff Matrix, readers will be able to appreciate the strategic thinking behind new product launches they encounter.
4. Diversification Strategy: A Critical Component of the Ansoff Matrix
Defining Diversification Strategy
Begin by defining diversification within the Ansoff Matrix context. This strategy involves developing new products for new markets, representing the highest risk quadrant in the matrix. It’s typically chosen when market opportunities are limited in the current market or the company seeks to leverage its competencies and resources into an unfamiliar market.
Types of Diversification Strategy
There are two types of diversification strategies – related and unrelated. Related diversification is when a company expands into a new market that is somewhat related to its existing business activities. Unrelated diversification, on the other hand, refers to expanding into completely new markets, which are unrelated to its existing business activities.
Advantages of Diversification Strategy
Discuss the potential advantages of diversification, such as reducing risk by spreading it over different industries, the potential for higher growth and profitability, better chances of survival in case the primary industry goes through a downturn, and maximizing the use of excess resources.
Risks and Challenges of Diversification Strategy
However, diversification also comes with significant risks and challenges. This can include increased complexity in management, high costs of entering a new market, unfamiliarity with the new market leading to potential missteps, and the potential for brand dilution.
Examples of Successful Diversification Strategy
End with some examples of successful diversification strategies. An example could be Virgin Group, which has successfully diversified into many sectors such as music, airlines, telecommunications, and even space travel.
Diversification represents a significant step for any company, requiring careful planning and execution. By detailing this strategy through the lens of the Ansoff Matrix, readers can gain insights into how businesses expand and enter entirely new markets.
5. Real-world Examples of the Ansoff Matrix
Market Penetration: McDonald’s
In recent years, McDonald’s has focused on increasing sales in existing markets by remodeling restaurants, extending store hours, and increasing advertising for their breakfast menu. These actions are all examples of market penetration strategies, aiming to increase the use of existing products among current customers.
Market Development: Spotify
Spotify entered the Indian market in 2019, taking its existing product – a music streaming service – into a completely new market. This move represented a market development strategy, where existing products are introduced to new markets.
Product Development: Google
Google, originally known for its search engine, has developed a range of new products for its existing user base over the years. Examples include Google Docs, Google Sheets, and Google Slides, all created to keep users within Google’s ecosystem, demonstrating an effective product development strategy.
Diversification: Amazon
Amazon’s move from an online book retailer to a comprehensive e-commerce store, cloud service provider, and streaming service provider is a great example of diversification. They have continually introduced new products to new market segments, such as when they launched Amazon Web Services (AWS) to target businesses for cloud computing services.
These real-world examples help your readers understand the application of the Ansoff Matrix in varied business scenarios. They serve to illustrate the strategic decisions companies make for growth and how the Ansoff Matrix can be used as a guiding framework.
6. The Role of the Ansoff Matrix in Strategic Marketing Planning
The Ansoff Matrix as a Strategic Tool
Begin by reiterating the significance of the Ansoff Matrix as a strategic tool for businesses. It allows them to visualize potential growth opportunities and align their marketing strategies accordingly.
Understanding Market and Product Possibilities
The matrix helps businesses understand the dynamics between markets and products. With its help, companies can decide whether to focus on market penetration, market development, product development, or diversification.
Risk Assessment and Management
Another crucial aspect of the Ansoff Matrix is its inherent risk assessment. From market penetration (least risky) to diversification (most risky), the matrix can be used as a tool for risk management in strategic planning.
Guiding Resource Allocation
By defining growth strategies, the Ansoff Matrix can also guide resource allocation in businesses. For example, a company focusing on product development might allocate more resources to R&D, while one targeting market development might invest more in market research and advertising in new markets.
Facilitating Decision-making
The Ansoff Matrix aids in decision-making by offering a structured approach to evaluating opportunities. This can be especially beneficial in strategic marketing planning, where deciding on the best growth strategy is crucial.
By explaining the role of the Ansoff Matrix in strategic marketing planning, you provide your readers with insights into how businesses leverage this tool to drive their growth and success. It will help them understand the practical significance of the matrix in the business world.
7. The Ansoff Matrix for the Digital Age
The Digital Transformation
Begin by highlighting the impact of the digital revolution on business operations, markets, and products. Explain how digital technologies have created new markets and have changed how products are created, marketed, and delivered.
Adapting the Ansoff Matrix
Talk about how the Ansoff Matrix can be updated to consider digital factors. For instance, digital technologies have blurred the lines between ‘existing’ and ‘new’ markets and products due to factors like online marketplaces and digital products/services. This new reality requires a more flexible application of the matrix.
Digital Market Penetration
This strategy can now include digital marketing campaigns aimed at increasing the use of existing products or services among the existing digital customer base. It could also involve improving the online user experience to increase customer engagement and retention.
Digital Market Development
This strategy could involve expanding into new digital marketplaces or platforms. For instance, a business that sells products through its own website might start selling on Amazon or eBay to reach a new online market.
Digital Product Development
With the advent of digital technologies, this strategy can involve creating new digital products or services for the existing market. For instance, a physical newspaper transitioning to an online version or a retail store launching an e-commerce platform.
Digital Diversification
This strategy might involve developing new digital products for new online markets. For instance, a brick-and-mortar clothing store might develop a mobile app game that promotes its products to a new market segment.
By updating the Ansoff Matrix for the digital age, you’ll help your readers understand how the traditional concept of this tool can be adjusted to address today’s digital reality. The flexibility of the Ansoff Matrix makes it a lasting strategic tool, adaptable to evolving business landscapes.
8. Case Study Analysis: Successful Implementation of the Ansoff Matrix
Starbucks: A Multi-faceted Growth Strategy
Start by explaining that Starbucks has successfully utilized all four strategies in the Ansoff Matrix to achieve tremendous growth.
Market Penetration: Starbucks Rewards
To increase sales among its existing customers, Starbucks launched the Starbucks Rewards program. It’s a loyalty program that encourages repeat purchases by offering rewards like free drinks or food items. This is a perfect example of a market penetration strategy.
Market Development: Starbucks’ Global Expansion
Starbucks has continuously entered new geographical markets since its inception. A notable example was its expansion into China, a market traditionally dominated by tea. This move is a clear instance of market development, where existing products are introduced to a new market.
Product Development: Launch of New Beverages
Starbucks frequently introduces new beverages to meet the evolving tastes and preferences of its existing customers. For example, the launch of a line of ‘Refreshers’ beverages offered customers a new, lighter caffeinated drink option, exemplifying product development strategy.
Diversification: Starbucks Evenings and Teavana
Starbucks has also ventured into new markets with new products. An example was the launch of ‘Starbucks Evenings,’ a program that offered wine and beer in select stores. Another example is its acquisition of Teavana, moving into the tea market. These actions represent diversification strategies.
By presenting this case study of Starbucks, you’ll be able to show the Ansoff Matrix in action, thereby helping your readers see its practical application and understand how it contributes to a company’s growth strategy.
9. Incorporating the Ansoff Matrix into Your Business Strategy
Understanding Your Current Situation
Before using the Ansoff Matrix, it’s essential to have a clear understanding of your current products and markets. Analyze your existing market share, customer base, and product range.
Analyzing Opportunities
Use the Ansoff Matrix to identify potential growth opportunities. Depending on your business goals and risk appetite, choose between market penetration, market development, product development, or diversification. Each option carries its own risks and rewards.
Performing a SWOT Analysis
Alongside the Ansoff Matrix, conduct a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) of your business. It can offer valuable insights that feed into your strategic decision-making.
Considering Resources and Capabilities
When choosing a strategy, ensure your business has the necessary resources and capabilities. For example, if you’re considering diversification, do you have the resources to develop new products? Or, if market development is your strategy, can your business handle the demands of a new market?
Regular Review and Adjustment
Strategic planning is an ongoing process. Regularly review your strategies in light of changing market conditions, customer preferences, and business performance. Be ready to adjust your strategy based on these reviews.
By following these steps, businesses can effectively incorporate the Ansoff Matrix into their strategic planning. It’s a powerful tool that can guide their growth trajectory and help them make informed strategic decisions.
10. Clearing Up Common Misconceptions about the Ansoff Matrix
Misconception 1: The Ansoff Matrix Guarantees Success
While the Ansoff Matrix is a useful tool for strategic planning, it does not guarantee success. It provides a framework for thinking about growth opportunities, but the eventual success of any strategy depends on execution, market conditions, and other factors.
Misconception 2: The Ansoff Matrix is Only for Large Corporations
While large corporations often use the Ansoff Matrix, it is also beneficial for small and medium-sized businesses. Any organization, regardless of its size, can use the matrix to explore potential growth strategies and consider the associated risks.
Misconception 3: The Ansoff Matrix is a Stand-alone Tool
Although the Ansoff Matrix is powerful, it should be used in conjunction with other business tools and analyses for the best results. For example, it can be used alongside a SWOT analysis or PESTEL analysis to provide a comprehensive overview of strategic options.
Misconception 4: The Ansoff Matrix Strategies are Mutually Exclusive
While the Ansoff Matrix presents four distinct strategies, in reality, businesses often pursue a mix of these strategies. For instance, a company might focus on market penetration in one product line while pursuing product development in another.
Misconception 5: The Ansoff Matrix is Outdated
While the Ansoff Matrix is a relatively old model (developed in 1957), it is not outdated. It remains a relevant and valuable tool in strategic planning. However, like any model, it needs to be adapted and interpreted in light of current business realities, including digital transformation.
By dispelling these misconceptions, you’ll help your readers gain a more accurate and nuanced understanding of the Ansoff Matrix, which will enable them to use it more effectively in their strategic planning.
Conclusion:
The Ansoff Matrix remains a timeless and potent tool for businesses seeking strategic growth. By understanding and correctly implementing the principles of market penetration, market development, product development, and diversification, companies can navigate their growth path more effectively. Although it’s not a foolproof formula for success, it provides a framework for evaluating potential growth opportunities and assessing associated risks. In a world of evolving markets and digital transformation, the matrix continues to be a vital instrument for businesses, from start-ups to multinational corporations, to make informed, strategic decisions.
