- 02/09/2023
- Posted by: Thamizharasu Gopalsamy
- Category: Management
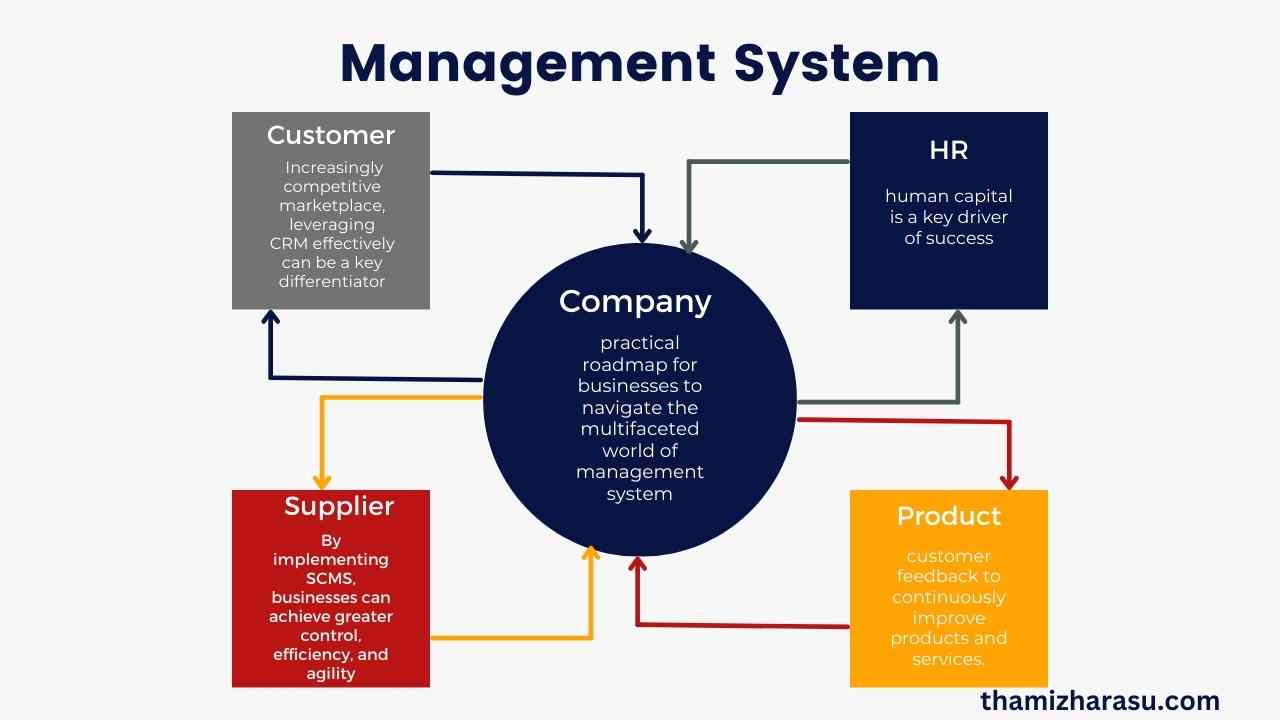
In today’s dynamic business environment, the term management system has become synonymous with success, efficiency, and growth. A management system is more than a mere tool; it’s the backbone that aligns various facets of an organization, streamlining operations, fostering innovation, and driving profitability. From small startups to multinational corporations, the implementation of an effective management system has become a critical need. This comprehensive guide explores the various components, methodologies, and futuristic trends in management systems, providing insights for entrepreneurs, leaders, and professionals seeking to leverage these powerful frameworks.
Management System Explainer Video
1 The Evolution of Management Systems: A Historical Perspective
Introduction
Management systems have played a crucial role in shaping the way businesses function and evolve. From primitive methods of organization to today’s complex technological frameworks, the journey of management systems has been remarkable. This article explores the fascinating historical perspective of management systems, unraveling how they have transformed over the years to suit modern business needs.
1. Primitive Era: Informal Management Systems
During ancient times, management systems were largely informal, relying on traditions and customs to guide organizational behavior. This phase laid the groundwork for more structured management as societies became more complex.
2. Industrial Revolution: The Birth of Formal Management Systems
The onset of the Industrial Revolution brought about the need for formal management structures. Pioneers like Frederick Taylor and Henri Fayol laid down principles that emphasized efficiency, division of labor, and hierarchical organization.
3. PostWar Era: Focus on Human Relations
The mid 20th century saw a shift towards human relations within management systems. Theories from scholars like Elton Mayo emphasized the importance of social factors and employee motivation, moving away from rigid, mechanical approaches.
4. Technological Advancements: Integration of Computers and Automation
With the rise of computer technology, management systems began to evolve towards automation and data-driven decision-making. Tools like ERP and CRM systems became essential components, enabling greater control and analysis.
5. Globalization Era: CrossCultural Management Systems
As businesses expanded globally, the need for adaptable and cross-cultural management systems grew. This era marked the integration of diverse practices and a focus on flexibility and adaptability to various cultural norms.
6. Current Trends: AI, Cloud Computing, and Agile Management
Today’s management systems are marked by the integration of artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and agile methodologies. These trends have led to more responsive, adaptive, and intelligent management practices that align with the rapidly changing business environment.
Conclusion: The evolution of management systems is a fascinating journey that reflects the changing dynamics of human society, technology, and business needs. From informal practices in the primitive era to today’s sophisticated technological frameworks, management systems have continuously adapted and grown.
Understanding this historical perspective not only provides insights into the foundations of modern management but also offers a lens through which to view future trends. As we look forward to the continued evolution of management systems, one thing is clear: adaptability, innovation, and humancentric approaches will remain at the heart of successful management practices.
2. Management System in Small Businesses: A Comprehensive Guide.
Introduction
Implementing a management system in a small business is a vital step in ensuring efficiency, growth, and sustainability. Unlike larger corporations, small businesses often face unique challenges that require tailored solutions. This comprehensive guide aims to assist entrepreneurs and small business owners in implementing an effective management system, from understanding the need to following through with continuous improvement.
1. Understanding the Need for a Management System
Identify Business Goals: Understand what you want to achieve with the management system.
Analyze Current Processes: Assess existing business processes and identify areas of improvement.
2. Selecting the Right Management System
Evaluate Different Systems: Consider various management systems that suit your industry and business size.
Choose a Scalable Solution: Opt for a system that can grow with your business.
3. Developing the Framework
Create Organizational Structure: Define roles and responsibilities.
Develop Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Write clear and concise guidelines for all critical business operations.
4. Implementing Technology Solutions
Select Appropriate Tools: Choose software that aligns with your business needs.
Train Staff: Ensure that your team understands how to use the tools effectively.
5. Monitoring and Evaluation
Set Performance Metrics: Define what success looks like.
Regularly Review Performance: Conduct ongoing assessments to ensure that the system is meeting its objectives.
6. Continuous Improvement
Encourage Feedback: Foster a culture where staff can suggest improvements.
Implement Changes: Regularly update the system to reflect new insights and changing business needs.
Conclusion: Implementing a management system in a small business is a process that requires careful planning, consideration of unique needs, and a commitment to ongoing evaluation and improvement. By following this step-by-step guide, entrepreneurs can create a tailored management system that supports their business goals and fosters a culture of efficiency and growth.
3. Sales and Marketing within a Unified Management System.
Introduction
In today’s competitive business environment, integrating sales and marketing functions within a unified management system is crucial for success. This alignment brings cohesiveness, improves communication, and ensures that both departments work towards common goals. This article will explore the benefits of this integration and provide methods to achieve it within a single management system.
1. Understanding the Need for Integration
Breaking Down Silos: Traditional separation between sales and marketing can lead to miscommunication and conflicting goals.
Unified Vision: Aligning both functions ensures a consistent approach to market positioning and customer engagement.
2. Benefits of Integration
Enhanced Collaboration: Encourages regular communication and collaboration between teams.
Improved Customer Experience: Aligns messaging and strategies across the customer journey.
Streamlined Processes: Reduces duplication and encourages efficiency through shared tools and data.
3. Methods of Integration
Developing Shared Goals: Creating common objectives that both sales and marketing can rally around.
Implementing Unified Technology: Utilizing a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system that both functions can access and manage.
Regular CrossDepartment Meetings: Encouraging dialogue and collaboration through regular meetings and joint projects.
4. Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Cultural Differences: Addressing potential differences in approach and mindset between sales and marketing.
Data Integration: Ensuring that data is shared and accessible across both functions.
Measuring Success: Developing shared metrics to gauge success and encourage accountability.
5. Case Studies and Success Stories
Sharing real-life examples where integration has led to significant business growth and customer satisfaction.
6. Continuous Improvement and Adaptation
Regular Review: Constantly reviewing the integration process and making necessary adjustments.
Fostering Innovation: Encouraging continuous improvement and innovation within the integrated system.
Conclusion: Integrating sales and marketing within a unified management system is not just a trend but a strategic necessity. It fosters alignment, enhances efficiency, and ultimately leads to better results for the business. By understanding the benefits, implementing effective methods, and committing to continuous improvement, businesses can leverage this integration to gain a competitive edge in the market.
4. Human Resource Management Systems (HRMS)
Introduction
In an era where human capital is a key driver of success, Human Resource Management Systems (HRMS) have become indispensable tools for businesses. By automating and optimizing HR functions, HRMS not only simplifies administrative tasks but also contributes to employee engagement and productivity. This article delves into the functionalities and benefits of HRMS, demonstrating how it can be a game-changer for modern organizations.
1. What is HRMS? An Overview
Definition: Explaining what HRMS entails, including its integration of human resource activities and IT.
Core Functions: Outlining the main functionalities such as recruiting, payroll, performance evaluation, and more.
2. Enhancing Employee Engagement with HRMS
Personalized Employee Portals: Enabling employees to access their information, benefits, and development plans.
Continuous Feedback Mechanism: Facilitating ongoing communication and feedback between employees and management.
Career Development Tools: Offering resources for continuous learning and career growth.
3. Boosting Productivity Through Efficiency
Automating Administrative Tasks: Reducing manual work in areas like payroll, attendance tracking, and benefits administration.
DataDriven Decision Making: Utilizing analytics to make informed HR decisions.
Integration with Other Systems: Aligning HRMS with other management systems for seamless operations.
4. Key Features to Look for in an HRMS
User-Friendly Interface: Emphasizing ease of use for both HR professionals and employees.
Scalability: Choosing a system that can grow with the business.
Compliance Management: Ensuring adherence to legal and regulatory requirements.
5. Implementing HRMS: Best Practices
Needs Analysis: Identifying specific organizational needs before selecting an HRMS.
Training and Support: Providing necessary training and ongoing support to ensure successful implementation.
Regular Upgrades and Maintenance: Keeping the system up to date with the latest features and security measures.
6. Challenges and Solutions
Data Security and Privacy: Addressing concerns and implementing robust security measures.
Change Management: Managing the transition smoothly to avoid resistance from employees.
Conclusion: Human Resource Management Systems (HRMS) represent a pivotal shift in how businesses manage their most valuable asset: their people. By enhancing employee engagement, streamlining processes, and providing actionable insights, HRMS offers a robust solution for modern HR challenges.
Whether a business is just starting its HRMS journey or looking to optimize an existing system, understanding the capabilities, best practices, and potential challenges is essential. With the right approach and tools, HRMS can be a catalyst for creating a more engaged, productive, and satisfied workforce.
5. Management System Standards: ISO Certifications and Compliance
Introduction
In the competitive and rapidly changing business landscape, adhering to internationally recognized management system standards is paramount. These standards, such as ISO certifications, ensure quality, efficiency, and consistency within organizations. This article offers a detailed insight into various management system standards, focusing on ISO certifications, and elaborates on the importance of compliance for businesses across different industries and sizes.
1. Understanding Management System Standards
Definition and Scope: Explanation of what management system standards are and their importance in the global business context.
Key Standards: Overview of various ISO standards, including ISO 9001 (Quality Management), ISO 14001 (Environmental Management), ISO 27001 (Information Security Management), and others.
2. Benefits of ISO Certifications
Enhanced Reputation: Building trust with customers and stakeholders through internationally recognized standards.
Improved Efficiency: Streamlining processes and enhancing productivity.
Regulatory Compliance: Meeting legal requirements and reducing risks of penalties.
3. The Process of Achieving ISO Certification
Gap Analysis: Identifying areas that need improvement to meet the desired standards.
Implementation: Developing and integrating processes and procedures in line with ISO requirements.
Auditing: Regular internal and external audits to ensure continuous adherence.
Certification: Obtaining the certification from an accredited body after successful evaluation.
4. Maintaining Compliance
Continuous Improvement: Regularly updating and improving systems to stay aligned with standards.
Employee Training: Educating staff on the importance of standards and their roles in maintaining compliance.
Monitoring and Reporting: Using metrics and reporting tools to track progress and identify areas for improvement.
5. Challenges and Solutions in Compliance
Resource Constraints: Addressing the challenges of time, money, and expertise in implementing and maintaining standards.
Changing Regulations: Adapting to evolving regulatory landscapes and maintaining compliance.
6. Case Studies and RealWorld Applications
Providing real-life examples of businesses that have successfully implemented and benefited from ISO certifications.
Conclusion: Management system standards, particularly ISO certifications, are more than just badges of honor; they are vital components in building a resilient, efficient, and trustworthy business. Compliance with these standards not only enhances an organization’s reputation but also provides a structured framework for continuous improvement and excellence.
In today’s globalized market, where customers and partners seek assurance of quality and consistency, adherence to ISO standards can be a strategic advantage. With the right approach, resources, and commitment, businesses of all sizes can leverage these standards as tools for growth and sustainability.
6 Risk Management Systems: Strategies and Tools for Identifying and Mitigating Business Risks.
Introduction
Risk is an inherent part of any business operation, and the ability to identify, assess, and mitigate risks is crucial for long-term success and sustainability. Risk management systems provide a structured approach to managing uncertainties that could negatively impact an organization’s objectives. This article offers an in-depth look at the importance of risk management systems, along with tools and strategies to implement them effectively.
1. Understanding Risk Management Systems
Definition and Scope: Explaining the concept of risk management and its relevance to businesses of all sizes.
Types of Risks: Overview of various risks, including operational, financial, strategic, compliance, and more.
2. Benefits of a Comprehensive Risk Management System
Proactive Approach: Enabling businesses to foresee potential issues and take preventive measures.
Resource Optimization: Allocating resources effectively by understanding and prioritizing risks.
Enhanced Decision Making: Making informed decisions backed by thorough risk analysis.
3. Strategies for Risk Identification and Assessment
SWOT Analysis: Utilizing Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats to evaluate risks.
Scenario Planning: Creating various what-if scenarios to understand potential outcomes.
Risk Matrix: Utilizing a risk matrix to categorize and prioritize risks based on severity and likelihood.
4. Tools for Implementing Risk Management
Risk Management Software: Exploring software solutions that offer real-time analysis and reporting.
Risk Registers: Creating centralized repositories for tracking and managing risks.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Utilizing metrics to measure the effectiveness of risk management strategies.
5. Developing a Risk Mitigation Plan
Risk Response Strategies: Understanding various responses, such as avoidance, mitigation, acceptance, and transference.
Action Plans: Creating detailed plans for addressing specific risks, including responsibilities, timelines, and resources.
Communication and Training: Ensuring that all stakeholders understand the risks and mitigation strategies.
6. Ongoing Monitoring and Review
Regular Assessments: Conduct ongoing risk assessments to adapt to changing business environments.
Lessons Learned: Implementing lessons learned from past experiences to continually improve the risk management process.
Conclusion: Risk management systems are essential instruments for navigating the uncertainties and complexities of the business world. By understanding the importance of risk management and implementing robust strategies and tools, organizations can build resilience, optimize performance, and foster a culture that values responsible decision-making.
With the right combination of foresight, planning, and continuous evaluation, businesses can turn risks into opportunities, driving growth and innovation in the face of challenges.
7. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems: Boosting Sales and Customer Satisfaction.
Introduction
In a world where customer expectations are constantly evolving, Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems have become an indispensable tool for businesses. CRM systems go beyond mere contact management, offering a holistic approach to customer engagement, sales optimization, and satisfaction. This article explores the functionalities, benefits, and best practices of CRM systems in enhancing customer relations and driving sales growth.
1. Understanding CRM Systems
Definition and Scope: Explaining what CRM systems are, including their role in managing customer interactions, sales processes, and more.
Components of CRM: Overview of various functionalities such as sales force automation, marketing automation, customer service, analytics, etc.
2. Boosting Sales Through CRM
Lead Management: Utilizing CRM to track and nurture leads through the sales funnel.
Personalized Marketing: Creating tailored marketing campaigns to target specific customer segments.
Sales Analytics: Analyzing sales data to identify trends, forecast sales, and optimize strategies.
3. Enhancing Customer Satisfaction with CRM
360Degree Customer View: Building comprehensive customer profiles to understand needs, preferences, and behaviors.
Omnichannel Support: Offering consistent and seamless support across various channels such as phone, email, chat, social media, etc.
Feedback and Surveys: Collecting and analyzing customer feedback to continuously improve products and services.
4. Integration with Other Management Systems
ERP Integration: Synchronizing CRM with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems for streamlined operations.
Social Media Integration: Connecting CRM with social platforms for enhanced social listening and engagement.
5. Selecting and Implementing a CRM System
Needs Assessment: Identifying specific business needs and choosing the right CRM solution.
Training and Adoption: Ensuring successful implementation through proper training and user adoption strategies.
Data Security and Compliance: Implementing robust security measures and adhering to relevant regulations.
6. Challenges and Solutions in CRM Implementation
Data Quality Issues: Addressing challenges related to data consistency and accuracy.
User Resistance: Overcoming resistance from employees and encouraging active usage.
Conclusion: Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems are more than just technology; they represent a strategic approach to building and sustaining meaningful customer relationships. By integrating CRM into a business’s overall management system, organizations can create personalized experiences, enhance customer satisfaction, and drive sales growth.
In an increasingly competitive marketplace, leveraging CRM effectively can be a key differentiator, helping businesses to stay ahead of the curve and foster lasting customer loyalty. Whether a company is considering implementing a CRM system or looking to optimize an existing one, understanding the capabilities, best practices, and potential challenges is essential for success.
8. Supply Chain Management Systems: Streamlining Operations for Success.
Introduction
In today’s globally connected business environment, an efficient and agile supply chain can be a critical factor for success. Supply Chain Management Systems (SCMS) offer an integrated approach to planning, executing, monitoring, and optimizing various supply chain functions. This article provides valuable insights into SCMS and how it can streamline operations, reduce costs, and contribute to business growth.
1. Understanding Supply Chain Management Systems (SCMS)
Definition and Components: An overview of SCMS and its main components, including procurement, production, distribution, warehousing, etc.
Importance of SCMS: Explanation of how SCMS can lead to a competitive advantage by improving efficiency, visibility, and collaboration.
2. Benefits of Implementing SCMS
Cost Reduction: Optimizing inventory, transportation, and procurement to reduce costs.
Enhanced Collaboration: Facilitating better communication and collaboration among suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers.
Realtime Visibility: Providing real-time insights into the supply chain for informed decision-making.
3. Strategies for Effective Supply Chain Management
Demand Forecasting: Utilizing predictive analytics to forecast demand accurately.
Supplier Relationship Management: Building strong relationships with suppliers to ensure reliability and quality.
Sustainability Initiatives: Implementing sustainable practices within the supply chain to reduce environmental impact.
4. Technological Tools in SCMS
Inventory Management Software: Using software to manage inventory levels and optimize stock.
Transportation Management Systems (TMS): Streamlining shipping and transportation activities.
IoT and Blockchain: Leveraging emerging technologies for enhanced tracking and authentication.
5. Challenges and Solutions in Supply Chain Management
Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating risks related to disruptions, compliance, supplier failures, etc.
Global Supply Chain Complexity: Navigating challenges related to international regulations, tariffs, cultural differences, etc.
6. Selecting and Implementing SCMS
Needs Analysis: Assessing specific business needs to choose the right SCMS solution.
Integration with Other Systems: Ensuring seamless integration with existing management systems like ERP, CRM, etc.
Change Management: Effectively managing the organizational change that accompanies SCMS implementation.
Conclusion: Supply Chain Management Systems are at the core of modern business operations, offering an integrated approach to managing complex supply chain activities. By implementing SCMS, businesses can achieve greater control, efficiency, and agility, translating into reduced costs, increased satisfaction, and ultimately, growth.
In a world where supply chain disruptions can have far-reaching impacts, a robust SCMS is no longer an option but a necessity. Whether you are an established enterprise or a growing startup, understanding and leveraging SCMS can be a strategic move toward achieving business success and sustainability.
9. Evaluating the ROI of Your Management System: Metrics and Analytics.
Introduction
Investing in a management system is a significant decision for any business. Understanding the return on this investment (ROI) is essential to justify the expense and to ensure that the system is contributing to organizational success. This guide explores the methodology, metrics, and analytical tools that can help businesses evaluate the ROI of their management system effectively.
1. Understanding the Importance of ROI in Management Systems
Definition of ROI: An introduction to ROI and its relevance in assessing the value of management systems.
Aligning ROI with Business Goals: How ROI evaluation should tie into overall business objectives and strategic goals.
2. Identifying Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Operational Efficiency: Measuring improvements in workflow, automation, and productivity.
Customer Satisfaction: Assessing how the management system impacts customer engagement and satisfaction.
Revenue Growth: Analyzing the system’s contribution to increasing sales, upselling, or market expansion.
3. Metrics for Evaluating ROI
CostBenefit Analysis: Comparing the overall costs of implementing and maintaining the system against the benefits.
TimetoValue: Assessing how quickly the system delivers tangible results.
Lifecycle Value: Evaluating the long-term value and sustainability of the system.
4. Analytical Tools and Techniques
Analytics Software: Utilizing specialized software to gather and interpret data related to the management system’s performance.
Benchmarking: Comparing internal results with industry standards or competitors’ performance.
Predictive Analytics: Leveraging predictive models to forecast future ROI based on current trends.
5. Challenges in Measuring ROI
Data Quality and Integrity: Ensuring accurate and consistent data collection.
Intangible Benefits: Quantifying benefits that may not be directly measurable, such as employee morale or brand reputation.
Changing Business Environment: Adjusting ROI metrics to reflect changes in market conditions or business strategy.
6. Case Studies and RealWorld Examples
Success Stories: Highlighting examples where management system ROI evaluation led to strategic improvements.
Lessons Learned: Analyzing instances where ROI evaluation identified areas for enhancement or revealed unexpected insights.
10. Future of Management Systems: AI, Automation, and Agile Frameworks.
Introduction
In an era where technology and innovation are transforming businesses at an unprecedented pace, management systems are evolving to become more intelligent, automated, and agile. This guide offers an insightful exploration into the future of management systems, focusing on cutting-edge trends such as AI-driven analytics, automation, and agile methodologies that are defining the next generation of business operations.
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Management Systems
AIDriven Analytics: Leveraging machine learning and predictive analytics to provide deeper insights into business performance.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Enhancing interaction with management systems through voice and text-based interfaces.
AIPowered Automation: Utilizing AI to automate complex decision-making processes and routine tasks.
2. Automation and Robotics in Management Systems
Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Implementing robots to perform repetitive tasks, reducing errors and enhancing efficiency.
Smart Workflow Automation: Creating intelligent workflows that adapt to changing business environments.
Integration with IoT: Connecting with Internet of Things (IoT) devices to facilitate real-time monitoring and control.
3. Agile Methodologies in Management Systems
Adopting Agile Principles: Applying Agile methodologies to management systems for flexible and responsive operations.
Scrum and Kanban in Management: Implementing Scrum and Kanban frameworks to drive project management and continuous improvement.
Collaborative Platforms: Utilizing tools that foster collaboration, transparency, and rapid adaptation to changes.
4. Emerging Technologies Shaping the Future
Blockchain in Supply Chain Management: Enhancing security and traceability within supply chain management systems.
Virtual Reality (VR) in Training and Simulation: Implementing VR for immersive training and scenario planning.
Quantum Computing in Analytics: Exploring the potential impact of quantum computing on data analysis and optimization.
5. Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Data Security and Privacy: Addressing concerns related to data protection and privacy in an AI-driven environment.
Bias and Fairness in AI Models: Ensuring that AI algorithms are transparent, unbiased, and ethically sound.
Change Management and Adaptation: Navigating the organizational challenges associated with rapidly evolving technologies.
6. Case Studies and RealWorld Applications
Innovative Implementations: Examining businesses that have successfully integrated AI, automation, and agile frameworks.
Lessons from Failures: Analyzing instances where technology adoption did not go as planned, extracting key learning points.
Conclusion
The landscape of management systems is ever-evolving, offering unprecedented opportunities to transform the way businesses operate. Whether it’s embracing AI-driven analytics, implementing agile methodologies, or focusing on customer-centric strategies, the modern management system is a multifaceted powerhouse. Leaders who understand, adapt, and innovate within this space position their organizations for success, growth, and sustainability. The time to master the modern management system is now. With this guide’s insights, strategies, and real-world applications, you are empowered to navigate the complexities and capitalize on the immense potential of contemporary management systems.
Would you like to take your business to the next level? for free consultation submit the form below.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
