- 19/07/2023
- Posted by: Thamizharasu Gopalsamy
- Category: Sales
Introduction:
In the world of business, understanding and effectively managing the sales cycle is a key ingredient for success. From prospecting potential customers to closing deals and following up post-sale, every stage of the sales cycle plays a pivotal role in achieving your business goals. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of the sales cycle, providing actionable tips, strategies, and insights to help you optimize your sales process and drive business growth.
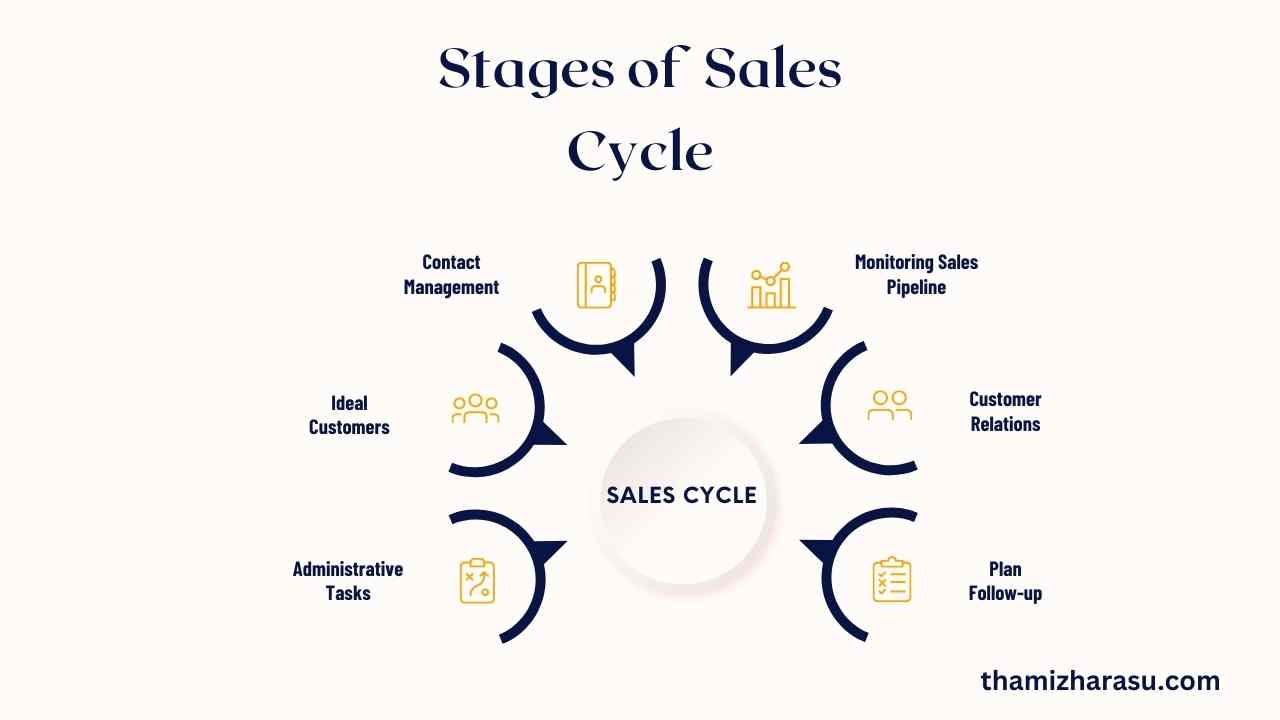
1. Understanding the Sales Cycle: A Comprehensive Overview
In the business world, the sales cycle is a critical concept that underlies every successful sales strategy. The sales cycle refers to the process that a company undertakes from the initial point of contact with a potential customer (or lead) to the closing of a deal. It encapsulates the steps that salespeople follow to convert leads into customers.
In essence, the sales cycle serves as a roadmap guiding sales teams in navigating the complex landscape of selling products or services. Every step of the cycle is crucial, as each represents a strategic move towards attaining a sale. Therefore, a clear understanding and mastery of the sales cycle are fundamental to sales success.
Typically, the sales cycle is composed of seven key stages:
1. Prospecting: This is the stage where the salesperson identifies potential customers or leads who might be interested in the product or service they’re selling.
2. Initial Contact: Once potential customers are identified, the salesperson makes the first contact. This could be through a phone call, email, social media, or even a face-to-face meeting.
3. Qualification: At this stage, the salesperson evaluates whether the prospect is a good fit for the product or service. This often involves understanding the prospect’s needs, budget, and buying authority.
4. Proposal: If the prospect qualifies, the salesperson presents a proposal that outlines how their product or service can address the prospect’s needs.
5. Negotiation: This stage involves discussing the terms of the deal, including pricing and delivery. The goal is to reach a mutually beneficial agreement.
6. Close: Once the terms are agreed upon, the sale is closed. The prospect becomes a customer.
7. Followup: After the sale is closed, the salesperson maintains contact with the customer to ensure satisfaction and explore possibilities for future sales.
While the length and complexity of the sales cycle can vary widely depending on the industry, product or service, and specific customer needs, these stages are generally universal. A well-managed sales cycle can lead to increased sales efficiency, improved customer relationships, and ultimately, business growth.
2. The Seven Stages of a Sales Cycle: An In-depth Analysis
Let’s take a closer look at the seven stages of a sales cycle, each constituting a crucial step toward making a successful sale:
1. Prospecting: Prospecting is all about identifying potential customers, also known as leads. This step involves extensive research to find individuals or businesses that may be interested in the product or service you’re offering. It involves understanding their needs, interests, and buying behavior. Successful prospecting lays the foundation for all subsequent stages in the sales cycle.
2. Initial Contact: After identifying your leads, the next step is to make the initial contact. This could be via a phone call, an email, a social media message, or even an in-person meeting. The primary purpose of this stage is to establish a connection with the lead, present your offering briefly, and gauge their interest.
3. Qualification: The qualification stage involves evaluating whether the lead is a good fit for your product or service. Factors that determine this include the lead’s needs, budget, decision-making authority, and readiness to buy. By qualifying leads, you can ensure that you’re focusing your time and resources on potential customers most likely to make a purchase.
4. Proposal: If a lead is deemed qualified, you move on to the proposal stage. Here, you present a detailed overview of how your product or service can address their needs and add value to their life or business. The proposal should be tailored to each prospect, addressing their specific challenges and goals.
5. Negotiation: Once the proposal is presented, negotiation usually ensues. This stage involves discussing the terms of the deal, including price, payment terms, delivery schedule, and after-sales service. It’s a delicate process that requires excellent communication and persuasion skills to reach a mutually beneficial agreement.
6. Close: The closing stage is where the deal is finalized, and the sale is made. The prospect agrees to the terms and becomes a customer. Closing may involve formalities such as signing a contract or making a payment.
7. Followup: The sales cycle doesn’t end with closing a sale. The follow-up stage involves staying in touch with the customer to ensure they’re satisfied with the product or service. This step is crucial for building lasting customer relationships, encouraging repeat business, and getting referrals.
Each stage in the sales cycle is a building block toward gaining a new customer. They provide a systematic and organized approach to selling and are adaptable to the unique needs and behaviors of your prospects. A deep understanding and effective execution of these stages can significantly improve your sales performance.
3. Prospecting in the Sales Cycle: Strategies for Success
Prospecting is the first and arguably one of the most important stages of the sales cycle. It involves identifying potential customers, or leads, who might have an interest in your product or service. Effective prospecting lays the groundwork for a successful sales cycle. Below, we discuss a few strategies to optimize your prospecting efforts:
1. Define Your Ideal Customer Profile (ICP): Before you start prospecting, it’s important to define your Ideal Customer Profile. This should be a detailed description of your target customer, including their industry, job title, company size, geographic location, and other relevant characteristics. Knowing your ICP allows you to focus your efforts on high-quality leads that are more likely to convert into customers.
2. Utilize Multiple Channels for Prospecting: In the digital age, there are multiple avenues available for prospecting. These include email, social media platforms, networking events, referrals, and even cold calling. Each channel has its strengths and weaknesses, and the best approach often involves using a combination of these channels to reach out to potential leads.
3. Leverage Technology: Sales prospecting tools and software can greatly streamline the prospecting process. These tools can help you automate tasks, track interactions with leads, and manage your pipeline effectively.
4. Develop a Strong Value Proposition: To catch the interest of potential customers, you need a compelling value proposition. This should be a clear statement that explains how your product or service solves customers’ problems, delivers specific benefits, and why it’s better than the competition.
5. Personalize Your Outreach: Leads are more likely to engage with personalized outreach efforts. Try to gather as much information as possible about your leads and use this information to tailor your outreach messages.
6. Follow Up Consistently: Prospecting is rarely a one-and-done process. Often, you’ll need to follow up with leads multiple times before getting a response. It’s important to be persistent without becoming a nuisance.
Remember, prospecting is about starting relationships. While the ultimate goal is to make a sale, your immediate objective should be to start a conversation and build rapport with potential customers. With the right strategies, prospecting can lead to a healthy pipeline of leads that can drive your sales success.
4. Initial Contact to Proposal: Navigating Early Sales Cycle Stages
Navigating the early stages of the sales cycle is crucial to your sales success. It involves several steps from making the initial contact to presenting the proposal. Here’s a closer look at these stages:
1. Initial Contact
The initial contact is your first interaction with a prospective customer. At this stage, you’re trying to capture their attention and ignite interest in your product or service. Here are a few best practices for this stage:
Research: Before reaching out, research the prospect thoroughly. Understand their business, needs, and challenges. This will help you tailor your communication and create a strong first impression.
Personalization: Make your interaction personalized. People appreciate it when you acknowledge their specific needs and challenges. Personalization also shows that you’ve taken the time to understand their situation.
Value Proposition: Convey your value proposition clearly. Explain how your product or service can solve their problem or meet their need. Keep your message concise and compelling.
2. Qualification
After the initial contact, the next step is to qualify the lead. This involves assessing whether the prospect is a good fit for your product or service. Key aspects of the qualification stage include:
Discovery: Ask questions to gather more information about the prospect. Understand their needs, budget, decision-making process, and timeframe for purchasing.
Assessment: Based on the information gathered, determine if the prospect is likely to buy your product or service. Remember, not every lead will be a good fit, and that’s okay. Focusing on high-quality leads will yield better results.
3. Proposal
Once a lead is qualified, you present them with a proposal. This stage requires careful planning and execution, as it directly influences the prospect’s decision to purchase. A few best practices for this stage include:
Solution-based approach: Frame your proposal around the prospect’s needs and how your product or service can address them. This shows that you understand their problem and have a suitable solution.
Transparency: Be transparent about your pricing and terms of service. Clear and honest communication can help build trust with the prospect.
Personalization: Tailor your proposal to the prospect. Highlight aspects of your product or service that align with their specific needs and goals.
These early stages of the sales cycle lay the groundwork for a successful sale. By approaching each stage thoughtfully and strategically, you can create a strong foundation for a productive relationship with your prospect.
5. Negotiation and Closing: Mastering the Critical Stages of the Sales Cycle
Negotiation and closing are critical stages in the sales cycle that require specific skills and techniques. Both stages need careful handling to ensure a successful outcome.
1. Negotiation
Negotiation is all about reaching a mutually beneficial agreement with the prospect. Here are some techniques for successful negotiation:
Preparation: Before entering a negotiation, prepare thoroughly. Know your product or service inside out, understand the prospect’s needs and wants, and be clear about what you’re willing to compromise on and what is non-negotiable.
Active Listening: During negotiation, listen more than you speak. Understanding the prospect’s viewpoint can help you provide suitable solutions and negotiate effectively.
Emphasize Value: Keep the focus on the value your product or service provides. If the prospect is focused on price, remind them of the benefits and value they’re getting.
Be Patient: Negotiation can take time. Be patient, and don’t rush the prospect into making a decision.
2. Closing
Closing is the stage where the deal is finalized. Here are some tips on how to effectively close a sale:
Clear Call to Action: A clear call to action can guide prospects toward finalizing the purchase. It could be as simple as, “Shall we proceed with the order?”
Address LastMinute Objections: Prospects may have last-minute objections or concerns. Address these promptly and confidently to reassure the prospect.
Create a Sense of Urgency: If appropriate, creating a sense of urgency can encourage prospects to make a decision quicker. This could be done by offering a limited-time discount or mentioning that the product or service is in high demand.
Confirm the Sale: Once the prospect agrees to the purchase, confirm the sale. This could involve signing a contract or making a payment.
Express Gratitude: After closing the sale, thank the customer for their business. This not only builds goodwill but also sets the stage for potential future business.
Mastering negotiation and closing techniques can significantly improve your sales results. With patience, practice, and these strategies, you can navigate these stages effectively and close more deals.
6. Following Up: The Often Overlooked Stage in the Sales Cycle
The follow-up is an essential but often overlooked stage in the sales cycle. This stage not only helps build long-term relationships with customers but can also lead to repeat business and referrals.
Following up involves staying in touch with the customer after the sale has been made, ensuring they’re satisfied with their purchase, and addressing any issues or concerns they might have. Here’s why it’s important:
Customer Satisfaction: By following up, you can ensure the customer is happy with their purchase and address any concerns promptly, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Opportunity for UpSelling and cross-selling: Followups can present opportunities for upselling or cross-selling, potentially leading to additional sales.
Referrals: Satisfied customers are more likely to refer your business to others, leading to potential new leads.
Here are some actionable tips on how to effectively execute the follow-up stage:
1. Time Your Followups: Timing is crucial when it comes to follow-ups. You don’t want to come off as pushy, but you also don’t want customers to feel neglected. A good practice is to follow up within a week after the sale, then adjust based on customer response and your company’s sales cycle.
2. Use Multiple Channels: Use different channels such as email, phone calls, or even in-person visits to follow up, based on what’s most appropriate and convenient for the customer.
3. Personalize Your Followups: Make your followups personal. Ask specific questions about their experience with the product or service, and show genuine concern for their satisfaction.
4. Provide Value: Each follow-up should provide value to the customer. This could be in the form of helpful tips, additional resources, or exclusive offers.
5. Ask for Feedback: Followups are a great time to ask for feedback. This not only shows customers that you value their opinions but can also provide valuable insights for improving your product or service.
By effectively executing the follow-up stage, you can maintain customer relationships, encourage repeat business, and drive growth in the long run. Remember, selling is not just about closing the deal but also about nurturing relationships and ensuring customer satisfaction.
7. Implementing a Sales Cycle: Best Practices for Businesses
Implementing a sales cycle in your business operations can significantly enhance sales performance and drive business growth. A well-structured sales cycle provides a systematic approach to selling and allows for better tracking, measurement, and optimization of the sales process.
Here are some best practices for implementing a sales cycle in your business:
1. Define Your Sales Cycle: The first step is to define your sales cycle. This involves identifying the stages that make sense for your business, based on your unique selling process, industry, and target audience. While the seven-stage model (prospecting, initial contact, qualification, proposal, negotiation, close, and follow-up) is common, your sales cycle might have fewer or additional stages.
2. Train Your Sales Team: Once you’ve defined your sales cycle, it’s important to train your sales team on it. Make sure they understand the purpose of each stage, what it entails, and the expected outcomes. This will ensure everyone is on the same page and working towards the same goals.
3. Leverage CRM Software: Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software can be a valuable tool for managing your sales cycle. It allows you to track where each prospect is in the cycle, store communication history, and generate insightful reports that can help improve your sales process.
4. Review and Refine: Regularly review your sales cycle to ensure it’s still serving your needs effectively. Analyze your sales data to identify bottlenecks or stages where prospects are dropping off. Then, make necessary adjustments to improve efficiency and effectiveness.
5. Foster Customer Relationships: A sales cycle isn’t just a business process—it’s also a customer journey. Always strive to provide value and build relationships at every stage of the cycle. This will not only improve your chances of making a sale but also foster customer loyalty and referrals.
Implementing a well-structured sales cycle can bring a host of benefits to your business, including increased sales efficiency, better forecasting, improved customer relationships, and ultimately, more sales and business growth. By following these best practices, you can leverage the power of the sales cycle to drive your business success.
8. Improving Your Sales Cycle: Tips for Streamlining and Optimization
Optimizing your sales cycle is a continuous process that can lead to significant improvements in sales performance and customer satisfaction. Here are some strategies for streamlining and optimizing your sales cycle:
1. Identify Bottlenecks: The first step towards optimization is identifying bottlenecks or hurdles in your sales cycle. These are stages where prospects are getting stuck or dropping off. Once identified, you can focus on finding ways to improve these stages.
2. Use Data and Analytics: Make use of CRM data and analytics to gain insights into your sales process. This can help you understand patterns, identify successful strategies, and pinpoint areas of improvement.
3. Train Your Sales Team: Regular training of your sales team is crucial for improving your sales cycle. Ensure they are equipped with the right skills and knowledge to effectively navigate each stage of the cycle.
4. Improve Lead Qualification: One common problem in sales cycles is spending too much time on unqualified leads. By improving your lead qualification process, you can ensure your sales team is focusing on leads that are most likely to convert into customers.
5. Leverage Automation: Automation can help streamline your sales cycle and reduce time-consuming tasks. Consider using sales automation tools for tasks like lead scoring, email marketing, follow-ups, and tracking sales activities.
6. Enhance Customer Communication: Clear and timely communication with customers can help move them through the sales cycle more smoothly. Ensure your sales team is communicating effectively and addressing customers’ questions and concerns promptly.
7. Test and Adjust: Sales cycle optimization is an ongoing process. Regularly test different strategies and make adjustments based on the results. This could involve trying out new sales techniques, using different communication channels, or adjusting the timing of follow-ups.
By focusing on these areas, businesses can streamline their sales cycle, improve efficiency, and ultimately, increase sales. Remember, the goal is not to rush prospects through the cycle but to create a smoother, more satisfying customer journey that leads to a successful sale.
9. Measuring Success in the Sales Cycle: Key Performance Indicators
Measuring the success of your sales cycle is crucial to understanding its effectiveness and identifying areas for improvement. This is usually done by tracking Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that reflect various aspects of your sales process. Here are some important KPIs that businesses should track:
1. Lead Conversion Rate: This measures the percentage of leads that become customers. A low conversion rate could suggest problems with your qualification process or sales approach.
2. Sales Cycle Length: This measures the average time it takes for a lead to go through your sales cycle, from initial contact to purchase. A long sales cycle might indicate inefficiencies in your sales process.
3. Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): This measures the total cost of acquiring a new customer, including marketing and sales expenses. If your CAC is high, you might need to find ways to streamline your sales process or improve your marketing efficiency.
4. Average Deal Size: This measures the average revenue generated from each sale. If your average deal size is small, you might want to focus on upselling or cross-selling opportunities.
5. Sales Funnel Leakage: This measures where in the sales cycle potential customers drop off. This can help identify stages in the sales cycle that need improvement.
6. Followup Rate: This measures how well your team is doing in terms of follow-ups. Followups are crucial in moving leads through the sales cycle, and a low follow-up rate can hinder your sales performance.
7. Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): This measures the total revenue you can expect from a customer over the length of their relationship with your business. CLV can help you determine how much you should invest in customer retention versus acquisition.
By tracking these KPIs, businesses can gain valuable insights into the effectiveness of their sales cycle. These metrics can also guide decision-making and strategy development, helping businesses optimize their sales process for better results.
10. Adapting the Sales Cycle in the Digital Age: Challenges and Opportunities
The digital age has significantly impacted the sales cycle, reshaping how businesses find leads, interact with prospects, and close deals. While it presents some challenges, it also offers numerous opportunities for enhancing the sales process.
Challenges in the Digital Age
Increased Competition: With the global reach of the internet, competition is fiercer than ever. Businesses need to constantly innovate and adapt to stay ahead.
Information Overload: Customers have access to a wealth of information online, which can make it harder for businesses to capture their attention and stand out.
Higher Customer Expectations: With digital tools at their disposal, customers expect faster responses, personalized interactions, and seamless experiences.
Opportunities in the Digital Age
Greater Reach: Digital tools enable businesses to reach a global audience, opening up new markets and opportunities.
Data and Analytics: Digital technologies provide a wealth of data that businesses can leverage to understand their customers better, tailor their sales approach, and optimize their sales cycle.
Sales Automation: Automation can streamline the sales process, reducing manual tasks and freeing up time for sales teams to focus on selling.
Social Selling: Social media platforms provide new avenues for finding leads and interacting with prospects, allowing businesses to engage with customers in a more relaxed and personal manner.
Improved Customer Relationships: With digital communication tools, businesses can stay in touch with customers more easily, improving communication and fostering stronger relationships.
Adapting Your Sales Cycle for the Digital Age
1. Leverage Digital Tools: Use CRM software, marketing automation tools, social media platforms, and other digital tools to streamline your sales process and enhance customer interactions.
2. Embrace Data: Use data analytics to gain insights into customer behavior, track sales performance, and optimize your sales cycle.
3. Focus on Customer Experience: In the digital age, customer experience is key. Make sure your sales process is customer-centric, offering seamless, personalized experiences across all touchpoints.
4. Invest in Online Presence: Make sure your business is easy to find and engage with online. This includes having a well-designed website, active social media profiles, and positive online reviews.
5. Provide Value Online: Use content marketing, social media, and other online platforms to provide value to customers beyond your products or services. This could be in the form of educational content, insightful blog posts, or helpful how-to guides.
The digital age brings both challenges and opportunities to the sales cycle. By understanding these, businesses can adapt their sales process, harness the power of digital tools, and thrive in the digital landscape.
11. Sales Cycle Explainer Video
Conclusion:
Mastering the sales cycle is a dynamic and ongoing process, demanding continuous learning, adaptation, and improvement. In the digital age, businesses have an array of tools and technologies at their disposal to enhance each stage of the sales cycle, making it more efficient and customer-centric. By understanding your sales cycle deeply, leveraging data for insights, focusing on providing value at every stage, and capitalizing on the digital tools available, businesses can create a robust, effective sales process that not only drives sales but also builds long-lasting relationships with customers.
