- 02/09/2023
- Posted by: Thamizharasu Gopalsamy
- Category: Management
Introduction:
In today’s unpredictable business landscape, understanding and managing risks is crucial for long-term success and resilience. The risk register, an essential tool in risk management, serves as a living document that identifies, assesses, and mitigates potential business challenges. From understanding its fundamental components to recognizing common pitfalls, this comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about the risk register. Entrepreneurs, project managers, and business leaders alike will discover actionable insights to make informed decisions and align risk management with strategic goals.
Risk Register Explainer Video
1. Understanding the Risk Register
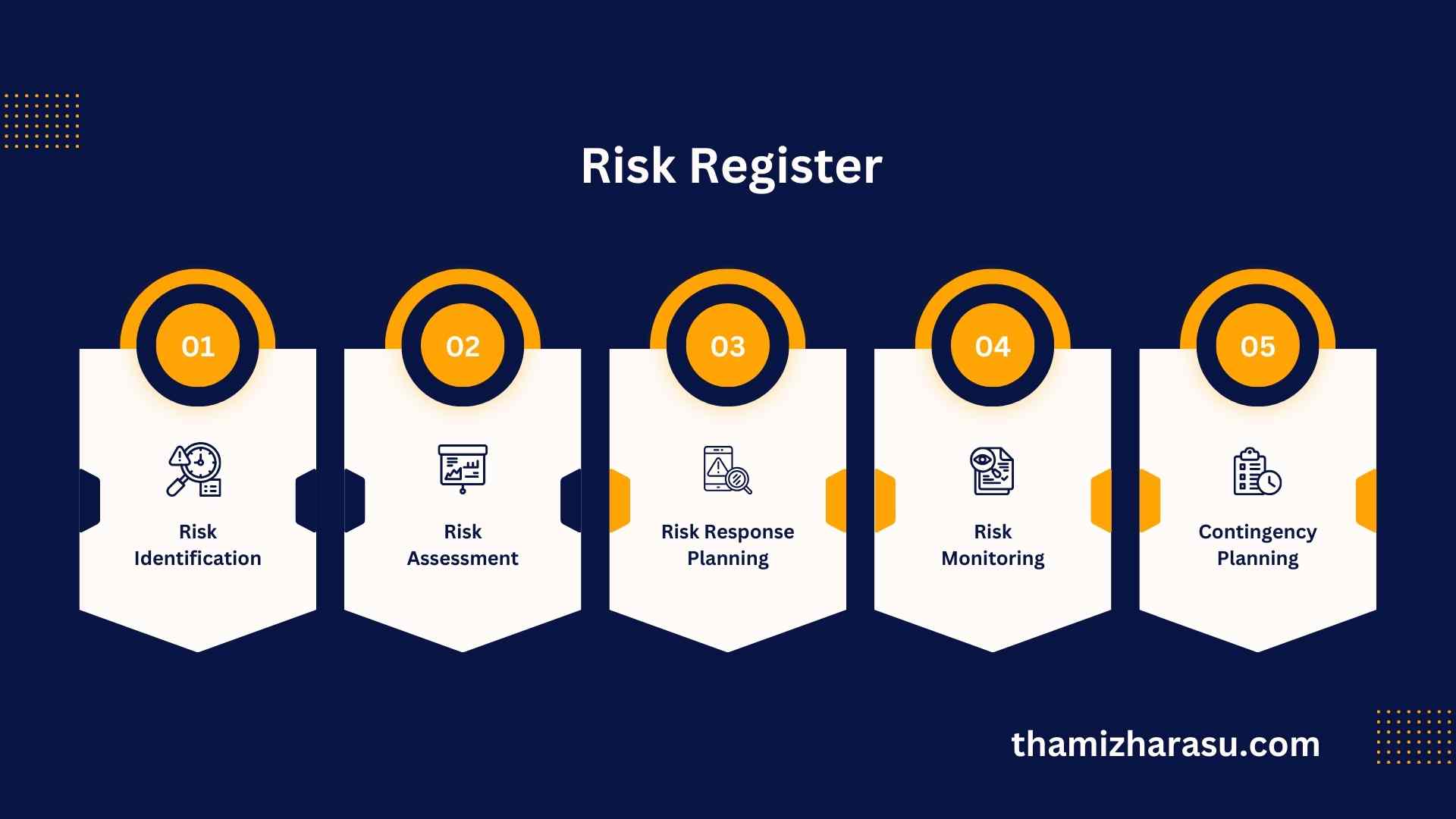
Introduction to Risk Register
A risk register, often considered the cornerstone of risk management, is a document used within project management and business planning. It serves as a valuable tool for identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks. Entrepreneurs and business leaders can utilize this register to ensure that potential threats and opportunities are systematically addressed.
Importance of Risk Register in Business
The risk register is not merely a document but a strategic asset in business planning. It aids in:
Identifying Risks: By listing potential risks, it provides a clear picture of what could go wrong, allowing for preemptive measures.
Risk Analysis: By categorizing and prioritizing risks, it helps in focusing on the most critical areas.
Mitigation Planning: By linking risks to corresponding mitigation strategies, it enables efficient risk management.
Tracking and Reporting: By providing a structure for regular review, it ensures that risks are continually monitored and controlled.
The risk register’s role extends beyond mere documentation; it is an essential element in decision-making and can be a competitive advantage for a proactive organization.
Components of a Risk Register
well-structured risk register typically consists of the following key components:
Risk Description: A clear explanation of the potential risk.
Risk Category: The classification of the risk into various domains such as operational, financial, or strategic.
Risk Impact: An assessment of how the risk might affect the project or business objectives.
Probability of Occurrence: An estimation of the likelihood of the risk occurring.
Mitigation Strategies: A detailed plan on how to address the risk, including resources required.
Status and Ownership: Information on who is responsible for managing the risk and its current status within the risk management process.
Conclusion: Understanding the risk register is paramount for entrepreneurs looking to build resilient and successful businesses. By breaking down the concept of a risk register and incorporating it into the organizational strategy, business leaders can better navigate the complex and uncertain environment they operate in. The systematic approach to identifying, analyzing, and managing risks not only reduces uncertainty but fosters a culture of proactive planning and continuous improvement.
2. How to Create a Risk Register: A StepbyStep Tutorial
Creating a risk register is an essential step in any project management or business planning process. It provides a systematic way to identify, analyze, and mitigate risks. Here’sstep-by-step-step guide to creating a risk register, complete with tools and templates that can be employed.
Step 1: Identify the Risks
Brainstorm with Your Team: Gather your team and use brainstorming sessions to identify potential risks.
Review Historical Data: Look at previous projects or industry benchmarks to recognize recurring risks.
Use Risk Identification Tools: Tools like SWOT analysis can be useful in pinpointing risks.
Step 2: Categorize the Risks
Define Risk Categories: Classify risks such as operational, financial, or strategic.
Use a Risk Breakdown Structure (RBS): An RBS can help organize risks into a hierarchical framework.
Step 3: Analyze the Risks
Determine Impact: Assess the potential impact of each risk on the project or business goals.
Estimate Probability: Evaluate the likelihood of each risk occurring.
Create a Risk Matrix: A risk matrix can help in visualizing the severity and likelihood of risks.
Step 4: Prioritize the Risks
Rank Risks: Based on the analysis, prioritize the risks in terms of their significance.
Focus on Critical Risks: Ensure that high-priority risks are addressed first.
Step 5: Develop Mitigation Strategies
Create Action Plans: Define specific strategies to mitigate or capitalize on each risk.
Assign Responsibility: Allocate risk ownership to specific team members or departments.
Step 6: Monitor and Update the Register
Regular Reviews: Schedule periodic reviews to assess the status of each risk.
Update as Necessary: Modify the risk register as new information becomes available or as risks evolve.
Tools and Templates
Various tools and templates are available to simplify the risk register creation process:
Microsoft Excel: Commonly used for creating risk registers due to their flexibility and ease of use.
Project Management Software: Tools like MS Project or Asana offer built-in risk register capabilities.
Templates: Many online resources offer free or paid risk register templates that can be customized.
Conclusion: Creating a risk register is a dynamic and vital process that requires careful planning, analysis, and continuous monitoring. By following this step-by-step tutorial, entrepreneurs and project managers can develop a comprehensive risk register tailored to their specific needs and objectives. By leveraging available tools and templates, the process becomes more streamlined and effective, leading to a more robust and resilient approach to risk management.
3. Risk Register in Project Management: Maximizing Success
Project management is fraught with uncertainties and potential obstacles. The risk register plays a crucial role in navigating these challenges, ensuring that projects are executed efficiently, and mitigating potential roadblocks. Here’s an exploration of how the risk register can be the key to maximizing success in project management.
What is a Risk Register in Project Management?
In the context of project management, a risk register is a living document that identifies, assesses, and plans for potential risks that could affect the project. It serves as a roadmap, enabling the project team to anticipate and respond to uncertainties proactively.
Why is a Risk Register Essential?
A risk register is not just a checklist but an integral part of the project management process for several reasons:
Visibility and Transparency: It offers a clear view of potential challenges, allowing stakeholders to understand the landscape of risks.
Alignment with Objectives: By aligning risks with project objectives, the risk register helps ensure that key goals remain in focus.
Facilitation of Communication: It acts as a communication tool, ensuring that team members are aware of and aligned on the risks and corresponding strategies.
Key Elements of a Risk Register in Project Management
The following elements are vital in a project management risk register:
Risk Identification: Detailed descriptions of potential risks, their sources, and triggers.
Risk Analysis: Qualitative and quantitative analysis of the impact and probability of risks.
Risk Response Plans: Specific strategies to mitigate, avoid, accept, or exploit the risks.
Monitoring and Controlling: Regular review and updating of the risk register to reflect changes in the project environment.
Strategies to Utilize Risk Register Effectively
Maximizing the effectiveness of a risk register in project management requires the following strategies:
Integration with Project Plans: Ensuring that the risk register is an integral part of the overall project plan.
Collaboration and Team Involvement: Engaging team members in risk identification and planning to leverage diverse insights.
Continuous Monitoring: Regularly reviewing and updating the risk register to ensure it remains relevant and actionable.
Tools and Techniques
Many project management tools offer risk register functionalities. Tools like JIRA, Trello, or specific risk management software can enhance the process by providing templates, analytics, and integration with other project management functions.
Conclusion: The risk register in project management is more than a mere compilation of potential risks; it’s a strategic tool that guides decision-making, fosters collaboration, and ensures alignment with project goals. By understanding its role and implementing it effectively, project managers can turn uncertainties into opportunities for growth and success. The risk register becomes a catalyst for proactive planning, helping projects navigate challenges and achieve their objectives with confidence and efficiency.
4. Integrating Risk Register with Business Strategy
In the ever-evolving business landscape, risk management must move beyond a siloed activity to an integral part of strategic planning. Integrating the risk register with overall business strategy allows organizations to align their growth plans with potential challenges and opportunities. Here’s how this alignment can be achieved and why it is essential for long-term success.
Alignment of Risk Register with Business Goals
Understanding Strategic Objectives: The first step in aligning the risk register with business strategy is understanding the organization’s long-term goals and core values.
Identifying Relevant Risks: Once the strategic direction is clear, it is vital to identify the risks that could directly impact these objectives.
Prioritizing Strategic Risks: Not all risks are equally critical; prioritizing them based on their relevance to strategic goals ensures focus and efficiency.
Risk Register as a Strategic Tool
Informed Decisionmaking: By incorporating a risk perspective, business leaders can make more informed decisions that consider both rewards and potential pitfalls.
Enhancing Agility: A strategic risk register allows the organization to respond more quickly to emerging risks or opportunities, thereby enhancing agility and competitiveness.
Fostering Innovation: By understanding risks, organizations can pursue innovative approaches with a clear understanding of the potential tradeoffs.
Integrating Risk Register into Planning Processes
Incorporating into Strategic Planning: The risk register should be a key input in the strategic planning process, ensuring that risks are considered in setting long-term direction.
Aligning with Budgeting and Forecasting: Financial planning can be more robust and realistic by integrating risk insights from the risk register.
Continuous Alignment with Business Changes: Regularly reviewing and updating the risk register ensures that it remains aligned with evolving business strategies and market conditions.
Leveraging Technology for Integration
Risk Management Software: Utilizing specialized software can facilitate the seamless integration of the risk register with various strategic planning tools and dashboards.
Data Analytics: Advanced analytics can provide deeper insights into risks and their potential impact on strategic objectives.
Conclusion: Integrating the risk register with business strategy is not a one-time exercise but an ongoing process that infuses risk consciousness into every aspect of strategic planning and execution. It ensures that risks are not just managed but leveraged as strategic insights that guide the organization towards its long-term goals. By aligning the risk register with overall business objectives, organizations can create a more resilient, agile, and growth-oriented strategic plan. It’s a move towards a holistic understanding of the business environment, where risks and opportunities are two sides of the same coin, both essential in shaping the path to success.
5. The Role of a Risk Register in Compliance and Legal Requirements
In today’s complex regulatory landscape, adherence to compliance and legal requirements is a must for businesses. The risk register, typically seen as a tool for managing business and project risks, also plays a crucial role in ensuring compliance with various regulations and avoiding legal pitfalls. Here’s a deep dive into how this works.
Understanding Compliance and Legal Risks
Definition of Compliance Risks: These are the risks associated with failing to adhere to laws, regulations, standards, or ethical practices that apply to an organization’s industry or jurisdiction.
Legal Implications: Noncompliance can lead to legal sanctions, fines, reputational damage, and even the loss of the right to conduct business.
Incorporating Compliance Risks into the Risk Register
Identification of Relevant Laws and Regulations: The first step is to identify all laws, regulations, and standards that apply to the organization, including industry-specific regulations, labor laws, environmental rules, etc.
Assessment of Compliance Risks: Evaluating the likelihood and potential impact of noncompliance. This includes understanding both immediate legal consequences and long-term reputational risks.
Utilizing the Risk Register for Compliance Management
Development of Compliance Policies: The risk register can guide the creation of internal policies that align with legal requirements.
Training and Awareness: Using the risk register to educate employees about compliance risks and the importance of adhering to internal and external rules.
Monitoring and Reporting: Regularly updating and reviewing the risk register to ensure continued compliance, and using it as a basis for required reporting to regulatory authorities.
Mitigation of Legal Risks through the Risk Register
Creating Legal Risk Response Plans: Defining specific actions to take if a legal risk materializes, such as engaging legal counsel or notifying regulatory authorities.
Leveraging Legal Expertise: Collaborating with legal professionals to ensure that the risk register accurately reflects the legal landscape and that appropriate mitigation strategies are in place.
Compliance and Risk Register in Different Industries
Healthcare: Compliance with patient privacy laws, medical licensing requirements, etc.
Finance: Adherence to banking regulations, anti-money laundering laws, etc.
Manufacturing: Compliance with environmental regulations, safety standards, etc.
Conclusion: The risk register’s role extends beyond traditional risk management to become a vital tool in ensuring legal compliance and adherence to regulatory requirements. By systematically identifying, assessing, and planning for compliance risks, organizations can build a strong legal foundation that supports their business objectives. In an era where regulatory scrutiny is ever-increasing, integrating compliance management into the risk register is not just a best practice but a strategic necessity. It’s a proactive approach that not only prevents legal issues but also strengthens the organization’s reputation and relationship with regulators, stakeholders, and the broader community.
6. Risk Register Technology: Top Software and Tools for Automation
The automation of the risk register process is becoming increasingly common as businesses seek more efficient and sophisticated ways to manage risks. Various software and tools have been developed to cater to this need. Here’s a review of some top technologies, exploring their features, pros, and cons.
1. RiskWatch
Features: RiskWatch offers comprehensive risk assessment, customizable risk matrices, and integration with other business tools.
Pros: Highly customizable, intuitive user interface.
Cons: Might be complex for small businesses, slightly higher learning curve.
2. SpiraPlan by Inflectra
Features: A robust tool that supports risk management in agile projects, with traceability and integration features.
Agile-focused, strong reporting capabilities.
Cons: Requires some familiarity with the agile methodologic Gies, which might be overkill for small projects.
3. LogicGate Risk Cloud
Featured-to-end-to-end solution with strong workflow capabilities, customizable risk libraries, and a wide range of templates.
Pros: Flexible and scalable, suitable for various industries.
Cons: Can be costly for smaller organizations ions, and requires proper configuration.
4. RiskWatch for Financial Services
Features: Tarinted in the financial sector, it offers compliance tracking, stress testing, and specialized financial risk modules.
Industry-specific civic functionalities, and integration with financial systems.
Cons: Limited to the financial industry, might be costly.
5. RSA Archer
Features: Offers a wide range of risk management functionalities, including compliance management, incident management, and more.
Pros: Comprehensive and robust, well-suited for large enterprises.
Cons: Complexity may deter small businesses and expensive licensing.
6. Resolver
Features: Designed for enterprise risk management with strong data analytics and visualization tools.
Pros: Intuitive design, strong support for data-driven decision-making.
Cons: May require training, better suited for large-scale operations.
Selecting the Right Tool: Considerations
Business Size and Complexity: Smaller businesses may prefer simpler tools, while large enterprises may need comprehensive solutions.
Industry Requirements: Some tools are designed for specific industries and may offer tailored functionalities.
Integration Needs: Consider how the tool will integrate with existing systems and processes.
Budget Constraints: Evaluate the cost of the tool against the value it brings to the organization.
Conclusion: Risk register technology is rapidly evolving, with a wide array of software and tools available to automate and enhance the risk management process. The key to success is selecting the right tool that aligns with the organization’s size, industry, complexity, and strategic objectives. By leveraging the power of automation, businesses can create a more agile, efficient, and insightful risk register process, turning risks into strategic insights that drive growth and resilience.
7. Using Risk Register for Financial Planning and Budget Control
In the intricate world of financial management, organizations continually strive for efficiency, control, and foresight. The risk register, often associated with general risk management, can play a critical role in financial planning and budget control. Here’s how this alignment works and why it’s vital for modern businesses.
Integration of Risk Register with Financial Planning
Understanding Financial Risks: The risk register helps in identifying and understanding the financial risks that can impact the organization’s revenue, expenses, investments, and liquidity.
Aligning with Financial Objectives: By connecting risks with financial goals, the risk register ensures that financial planning considers potential challenges and uncertainties.
Risk Register in the Budgeting Process
Informed Budgeting: Utilizing risk insights to create realistic budgets that factor in potential financial uncertainties, such as market fluctuations or regulatory changes.
Contingency Planning: Including risk mitigation strategies and contingency funds in the budget to handle unexpected financial challenges.
Risk Register in Financial Analysis and Forecasting
Risk-adjusted Forecasting: Using the risk register to create forecasts that incorporate potential financial risks, making predictions more robust and realistic.
Monitoring Financial Risks: Regularly updating the risk register to reflect changes in the financial landscape, allowing for timely adjustments to financial plans and strategies.
Risk Register in Financial Reporting and Compliance
Transparency in Reporting: Including risk information in financial reports enhances transparency and provides stakeholders with a comprehensive view of the organization’s financial health.
Compliance with Financial Regulations: The risk register can help ensure adherence to financial regulations, such as those related to financial disclosures or capital requirements.
Risk Register in Investment Decisionmaking
Riskaware Investing: Leveraging the risk register to understand the risks associated with various investment options, guiding more informed investment decisions.
Alignment with Investment Strategy: Ensuring that investment decisions align with the organization’s risk tolerance and overall investment strategy.
Risk Register and Cost Control
Identifying Cost Risks: Recognizing potential risks that could impact costs, such as supply chain disruptions or currency fluctuations.
Mitigating Cost Overruns: Implementing risk mitigation strategies to control costs and prevent overruns.
Tools and Techniques for Financial Risk Register
Specialized Software: Many financial management systems offer integrated risk register functionalities, designed to support financial planning, budgeting, and control.
Risk Modelling: Financial risk models can be incorporated into the risk register to provide quantitative insights into potential financial outcomes.
Conclusion: The risk register’s role in financial planning and budget control extends beyond traditional risk management, transforming it into a strategic financial tool. By systematically identifying, analyzing, and planning for financial risks, organizations can create financial strategies that are more resilient, flexible, and aligned with their goals. In an uncertain economic environment, the risk register becomes an essential instrument in steering financial success, ensuring that businesses can navigate financial challenges and opportunities with confidence and agility. Whether it’s budgeting, investing, cost control, or compliance, the risk register infuses financial management with a robust risk-aware approach, paving the way for sustainable growth and stability.
8. Case Studies: Success Stories of Utilizing Risk Register in Various Industries
The risk register has become a fundamental tool in various industries to identify, analyze, and manage risks. By sharing real-world examples, this section aims to highlight the diverse ways businesses have successfully implemented risk register processes, illustrating the benefits and insights that can be gained.
1. Healthcare Industry: Hospital Risk Management
Situation: A large hospital faced challenges in patient safety, compliance with healthcare regulations, and operational efficiency.
Solution: Implemented a comprehensive risk register to categorize risks, from patient care to regulatory compliance.
Outcome: Improved patient safety protocols, ensured compliance, and streamlined operations, leading to higher patient satisfaction.
2. Construction Industry: Mega Infrastructure Project
Situation: A construction company managing a multibillion-dollar infrastructure project needed to mitigate various risks, including delays, cost overruns, and safety concerns.
Solution: Utilized a risk register to identify potential risks and create contingency plans.
Outcome: Successful completion of the project on time and within budget, with minimized safety incidents.
3. Financial Sector: Global Bank’s Compliance Program
Situation: A global bank needed to comply with a complex set of international financial regulations.
Solution: Developed a risk register focused on compliance risks, integrating it with regular audits and monitoring.
Outcome: Enhanced compliance posture, reduced fines, and increased trust from regulators and customers.
4. Manufacturing Industry: Supply Chain Optimization
Situation: A manufacturing firm faced disruptions in its supply chain due to unforeseen events such as natural disasters and political instability.
Solution: Implemented a risk register that included a detailed analysis of supply chain risks, along with mitigation strategies.
Outcome: Increased supply chain resilience, reduced downtime, and improved supplier relationships.
5. Technology Sector: Cybersecurity Management for a Tech Startup
Situation: A growing tech startup needed to protect its intellectual property and customer data from cyber threats.
Solution: Created a risk register with a focus on cybersecurity risks, incorporating best practices and regular assessments.
Outcome: Enhanced security posture, protected critical assets, and built customer trust.
6. Energy Industry: Environmental Compliance for an Oil Company
Situation: An oil company required alignment with stringent environmental regulations and wanted to minimize environmental impact.
Solution: Utilized a risk register to identify environmental risks and develop strategies to mitigate them.
Outcome: Achieved compliance with environmental regulations and demonstrated corporate social responsibility.
Conclusion: These case studies showcase the versatility and efficacy of the risk register across various industries and scenarios. Whether managing patient safety in healthcare, ensuring compliance in finance, optimizing supply chains in manufacturing, or protecting assets in technology, the risk register has proven to be an invaluable tool. The success stories underline the importance of a tailored approach, where the risk register is designed and implemented to meet the specific needs and challenges of each industry. By learning from these examples, organizations in different sectors can draw insights and inspiration to create a risk register that not only mitigates risks but also contributes to strategic objectives and long-term success.
9. Risk Register Training: Developing Skills in Your Team
Training staff to effectively maintain and utilize a risk register is essential for an organization’s risk management strategy. By cultivating these skills within the team, businesses can ensure a more proactive and consistent approach to managing risks. Here’s how to embark on this critical training journey.
1. Understanding the Importance of Risk Register
Why Train: Explain why risk management and the risk register are essential for organizational success.
Benefits: Highlight the benefits of implementing a risk register, including informed decision-making and alignment with business goals.
2. Identifying Targeted Skill Sets
Core Skills: Determine the essential skills required for maintaining a risk register, such as risk identification, analysis, prioritization, and mitigation planning.
Customized Training: Tailor training to different roles within the organization, as different departments may have unique risk-related needs.
3. Designing the Training Program
Curriculum Development: Create a comprehensive curriculum that covers theoretical knowledge, practical skills, and best practices.
Training Formats: Consider various training formats, including workshops, webinars, on-the-job training, and e-learning modules.
4. Involving External Experts
Expert Guidance: Consider hiring risk management experts to provide specialized training and insights.
Industry Insights: Incorporate industry-specific risk management techniques and methodologies.
5. Implementing Practical Exercises and Simulations
Hands-on Learning: Include exercises and simulations that allow staff to practice maintaining a risk register in real-life scenarios.
Feedback and Evaluation: Provide continuous feedback and assessment to ensure skills are correctly developed and implemented.
6. Integrating Risk Register Training into Onboarding
Orientation: Integrate risk register training into the onboarding process for new employees to establish a risk-aware culture from the beginning.
Continuous Learning: Encourage ongoing learning through refresher courses and advanced training opportunities.
7. Utilizing Technology and Tools
Training Platforms: Leverage technology to deliver training through online platforms and tools that facilitate interactive learning.
Risk Register Software Training: Offer training on specific software and tools used within the organization to manage the risk register.
8. Measuring the Effectiveness of Training
Assessment Metrics: Develop clear metrics to evaluate the effectiveness of the training, such as improvement in risk identification, analysis, or mitigation.
Continuous Improvement: Regularly review and update the training program to ensure that it remains relevant and effective.
Conclusion: Risk register training is not merely about teaching staff how to fill out a template; it’s about instilling a mindset and a set of competencies that enable effective risk management. By carefully designing, implementing, and evaluating a training program that caters to the unique needs and goals of the organization, businesses can foster a culture where risks are systematically identified, analyzed, and managed. In doing so, they create a more resilient organization, ready to navigate the uncertainties of the business landscape. The training journey is a continuous one, requiring regular updates and a commitment to nurturing a risk-aware culture, where every team member plays a part in shaping the organization’s success.
10. Risk Register Mistakes: Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
While a risk register is an essential tool for any business’s risk management strategy, it is not immune to errors and missteps. Identifying common mistakes and understanding how to avoid them can greatly enhance the efficacy of the risk register. Below, we explore the common pitfalls and the corresponding solutions.
1. Incomplete or Vague Risk Identification
Mistake: Not identifying all potential risks or defining them too vaguely.
Solution: Employ systematic risk identification techniques, involve various stakeholders, and define risks clearly and specifically.
2. Ignoring Low Probability Risks
Mistake: Overlooking risks that have a low probability but could have a significant impact.
Solution: Consider all risks, regardless of probability, and evaluate them based on potential impact as well.
3. Lack of Regular Updates
Mistake: Failing to update the risk register regularly, making it stagnant and less useful.
Solution: Establish a routine for regular review and update of the risk register, adapting to changes in the business environment.
4. No Ownership or Accountability
Mistake: Failing to assign ownership for specific risks, leading to confusion and lack of responsibility.
Solution: Clearly assign ownership for each risk and ensure that those responsible are held accountable for monitoring and mitigation.
5. Ineffective Risk Mitigation Strategies
Mistake: Implementing generic or ineffective risk mitigation strategies.
Solution: Tailor risk mitigation strategies to specific risks and regularly evaluate their effectiveness.
6. Overcomplicating the Risk Register
Mistake: Creating a risk register that is overly complex and difficult to manage.
Solution: Keep the risk register streamlined and user-friendly, ensuring that it is a practical tool for all involved.
7. Neglecting Communication and Collaboration
Mistake: Failing to communicate and collaborate across different departments when managing risks.
Solution: Foster collaboration and communication across teams, and ensure that relevant parties are informed about risks and mitigation plans.
8. Ignoring Longterm Risks
Mistake: Focusing solely on immediate risks and ignoring long-term or strategic risks.
Solution: Incorporate long-term risks into the risk register and align them with the organization’s strategic objectives.
9. Lack of Alignment with Business Goals
Mistake: Creating a risk register that is disconnected from the overall business objectives and strategy.
Solution: Align the risk register with the organization’s goals, ensuring that it serves as a tool for strategic decision-making.
10. Overreliance on Software Tools
Mistake: Relying too heavily on software tools without understanding the underlying risk management principles.
Solution: While leveraging technology, ensure that the team understands the principles of risk management and actively engages in the process.
Conclusion: Mistakes in handling a risk register are not uncommon, but they can significantly undermine its effectiveness. By recognizing these common pitfalls and implementing thoughtful solutions, businesses can optimize their risk register to serve as a powerful tool for risk management. From clear risk identification to regular updates, from fostering collaboration to aligning with business goals, the risk register’s success hinges on attention to detail and a commitment to continuous improvement. Organizations that heed these insights can elevate their risk management practices, creating a more resilient and strategically aligned enterprise ready to navigate the complex and uncertain business landscape.
Conclusion:
The risk register is more than just a document; it’s a strategic ally in navigating the complex world of business risks. By understanding its nuances, employing best practices, and avoiding common mistakes, organizations can harness its full potential. Whether you’re starting a new venture, overseeing a project, or steering an established organization, the insights, and methodologies presented in this guide will empower you to master the risk register. As you embark on this journey, remember that effective risk management is an ongoing process, one that requires vigilance, collaboration, and continuous adaptation. Embrace the risk register as a vital part of your business toolkit and take a confident step towards a more secure and successful future.
