- 19/05/2023
- Posted by: Thamizharasu Gopalsamy
- Category: Management

Introduction:
The constantly evolving business landscape necessitates effective strategic management for any organization aiming for sustainable success. Strategic management, an all-encompassing approach to business planning and execution, serves as a blueprint for navigating the complex world of business. This comprehensive guide will delve into the core concepts of strategic management, its vital role in contemporary business, and the future trends that are set to redefine strategic planning and execution. From understanding the strategic management process and its various tools to exploring real-world examples of successful strategic practices, this guide aims to provide a holistic perspective on strategic management.
1. Understanding the Core Concepts of Strategic Management
Strategic management is a critical aspect of business administration, and understanding its core concepts is essential for anyone interested in the field. At its heart, strategic management involves the formulation and implementation of major goals and initiatives, based on consideration of resources and an assessment of internal and external environments in which the organization operates.
One of the first concepts to grasp in strategic management is the Vision. The vision sets out the organization’s long-term direction and aspiration. It paints a picture of what the organization aspires to be or achieve in the long run. It’s the organization’s guiding light, giving direction to all its strategic initiatives.
Following the vision is the Mission. While the vision is future-oriented, the mission focuses on the present and defines the organization’s purpose or reason for existence. It outlines what the organization does, for whom it does it, and how it does it. A clear mission acts as a unifying force, providing guidance to employees about what they are expected to achieve.
Next are the Objectives. These are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals that are derived from the mission and vision. They provide a sense of direction on a more operational level, giving employees clear tasks and targets to work towards.
Another fundamental concept in strategic management is Strategy Formulation. This involves determining the best course of action to achieve the organization’s mission, objectives, and ultimately, the vision. It includes processes like SWOT analysis, PESTEL analysis, and Porter’s Five Forces analysis, among others, to evaluate the organization’s position and decide on strategic direction.
Strategy Implementation is the next step in the strategic management process. It’s where the strategies and policies are put into action through the development of programs, budgets, and procedures. It requires an effective organizational structure, allocation of resources, and a supportive organizational culture to be successful.
Finally, the process concludes with Strategy Evaluation and Control, which involves monitoring and evaluating the progress toward strategic objectives and making necessary adjustments in strategy, implementation, or even objectives, based on actual performance and changing circumstances.
In today’s ever-changing business environment, strategic management is more important than ever. It provides a sense of direction, a roadmap if you will, to navigate the complex and dynamic landscape of business. It enables businesses to respond effectively to opportunities and challenges alike, thus ensuring their survival and success in the long run.
2. Strategic Management Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
Strategic management is a continuous process that directs an organization toward its goals. This process is a sequential series of analyses, decisions, and actions used to formulate and implement strategies. Here’s a step-by-step guide to the strategic management process:
1. Environmental Scanning:
This is the first step in the strategic management process. It involves a thorough analysis of the organization’s internal and external environment. Internal scanning, also known as organizational analysis, examines the resources, capabilities, and activities within the company. External scanning, on the other hand, looks at the broader business environment, including factors such as competition, market trends, and broader economic, political, and societal issues. Tools such as SWOT analysis, PESTEL analysis, and Porter’s Five Forces analysis can be used for this purpose.
2. Strategy Formulation:
Based on the insights gained from environmental scanning, the organization formulates its strategy. This involves setting long-term objectives and deciding on the strategic direction. Strategic choices could involve pursuing new markets, developing new products, or deciding on specific competitive strategies like cost leadership or differentiation.
3. Strategy Implementation:
Once the strategy is formulated, the next step is implementation. This involves developing an organizational design that supports the strategy, establishing strategic controls, and managing human resources effectively to execute the strategy. It also involves communicating the strategy throughout the organization and motivating employees to embrace and execute the strategy.
4. Strategy Evaluation and Control:
This is a critical step in the strategic management process where the implemented strategy is evaluated. The organization monitors internal and external events that affect strategy implementation, measures performance, and takes corrective actions if the actual performance deviates from the strategic objectives. It may involve altering the strategy or its implementation if the circumstances warrant it.
This process is not a one-off; it is iterative and ongoing, requiring continuous monitoring and evaluation. The world of business is dynamic and ever-changing, and the strategic management process is designed to help organizations navigate this complexity and steer them toward their goals effectively. Remember, strategic management isn’t a straight path to success; it’s a cycle of planning, execution, review, and adjustment.
3. The Role of SWOT Analysis in Strategic Management
SWOT Analysis is a vital strategic planning tool used in the realm of strategic management. The acronym SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. This analysis provides a structured method to evaluate the internal and external environment of an organization, leading to more informed decision-making and effective strategic planning.
Strengths: These are the internal attributes or resources of an organization that give it a competitive edge. Strengths could include a strong brand reputation, a loyal customer base, proprietary technology, or financial resources. Identifying these strengths allows an organization to leverage them to its advantage.
Weaknesses: These are also internal factors, but unlike strengths, they hinder an organization’s performance. Weaknesses could be anything from outdated technology, poor customer service, weak financial performance, to a lack of skilled personnel. Acknowledging these weaknesses is crucial to formulating strategies that help to mitigate their impact.
Opportunities: These are external factors that the organization could capitalize on for its benefit. Opportunities could include a new market, a favorable government policy, positive demographic shifts, or even competitors’ weaknesses. Recognizing these opportunities helps in formulating strategies that exploit them.
Threats: These are external factors that could pose challenges to the organization. Threats might be in the form of increased competition, changing consumer preferences, unfavorable government regulations, or economic downturns. Identifying threats is key to developing strategies that minimize their impact or enable the organization to sidestep them altogether.
So, how does SWOT analysis contribute to strategic management?
First, it provides a clear and concise overview of the organization’s current situation, both internally and externally. It offers a snapshot of the company’s capabilities and the challenges it faces.
Second, a SWOT analysis can help identify strategic directions. For instance, a strategy could be to leverage strengths to capitalize on opportunities (SO strategy), or use strengths to avoid threats (ST strategy). Alternatively, the organization could work on weaknesses to exploit opportunities (WO strategy), or minimize weaknesses and avoid threats (WT strategy).
Finally, SWOT analysis stimulates strategic thinking and aids in strategy formulation. It prompts the organization to think about its position and the strategies it needs to adopt to achieve its objectives, thus playing a crucial role in strategic management.
4. Leveraging PESTEL Analysis for Strategic Planning
PESTEL Analysis is an essential tool in strategic management that helps organizations understand the macro-environmental factors that could impact their operations. The acronym PESTEL stands for Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal factors. By assessing these factors, organizations can anticipate potential challenges and opportunities, aiding in strategic planning. Here’s how each element of PESTEL Analysis contributes to this process:
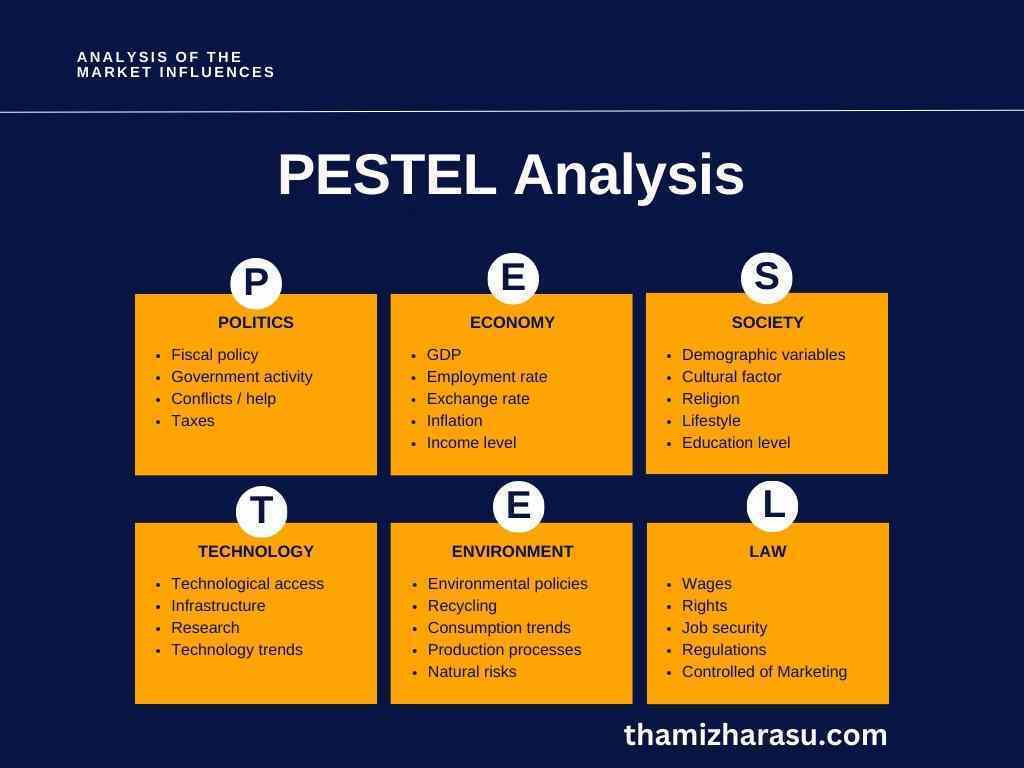
Political: This involves understanding the impact of government policies, regulations, political stability, and corruption levels on the organization. Political factors can greatly influence the feasibility and profitability of doing business. For example, changes in tax laws, trade tariffs, or political instability can significantly affect a company’s operations.
Economic: This examines the broader economic conditions such as inflation, unemployment, exchange rates, and economic growth. These factors can influence consumer purchasing power, demand, cost of capital, and therefore, profitability. For instance, during an economic downturn, customers may cut back on spending, impacting a company’s sales and profits.
Social: This looks at societal trends and influences, including demographics, consumer attitudes, cultural nuances, and lifestyle trends. These factors can affect customer needs and the size of potential markets. For example, an aging population may increase the demand for healthcare services.
Technological: This considers the impact of technological innovation, research and development, automation, and the rate of technological change. Technological factors can create new opportunities, help businesses to become more efficient, and drive innovation. For example, the advent of e-commerce has transformed the retail landscape, creating new business models and consumer behaviours.
Environmental: This focuses on ecological and environmental aspects such as weather, climate change, and sustainability. These factors can affect industries such as tourism, farming, and insurance, and have become more significant due to increased consciousness of climate change. For instance, companies are now expected to have environmentally friendly practices, impacting their reputation and potentially their sales.
Legal: This involves understanding laws and regulations that affect the industry and the organization. These include labor laws, health and safety regulations, data protection laws, and copyright laws. Legal factors can influence the company’s operations, cost of compliance, and risk level.
PESTEL Analysis aids strategic management by providing a holistic view of the external environment. By understanding these macro-environmental factors, organizations can make informed decisions, formulate effective strategies, and better prepare for the future. It allows them to align their strategies with the external environment, ensuring their strategic initiatives are not only feasible but also have the potential for success.
5. Strategic Management Tools and Techniques: An Overview
There are several strategic management tools and techniques that help businesses in their strategic planning process and execution. These tools provide a structured approach to strategizing, allowing businesses to identify their goals, measure performance, and track progress. Let’s discuss a few key tools:
Balanced Scorecard: The Balanced Scorecard is a strategic planning and management tool that allows organizations to align business activities with their vision and strategy, improve internal and external communication, and monitor performance against strategic goals. It provides a balanced view of organizational performance by looking at four perspectives: Financial (profit, revenue, ROI), Customer (customer satisfaction, retention), Internal Processes (productivity, efficiency), and Learning & Growth (employee satisfaction, retention).
Benchmarking: Benchmarking is the process of comparing an organization’s processes and performance metrics to industry bests or best practices from other companies. It can provide insights into areas where the organization can improve, promote a culture of continuous improvement, and help identify methods to achieve superior performance.
Scenario Planning: This is a strategic planning tool that helps organizations anticipate future events and plan for various plausible future scenarios. By imagining different futures, organizations can prepare for unexpected changes, mitigate risks, and seize opportunities. It encourages strategic thinking and improves decision-making.
SWOT Analysis: As discussed earlier, this tool helps identify Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats, enabling the organization to leverage its strengths, mitigate weaknesses, capitalize on opportunities, and minimize threats.
PESTEL Analysis: Also mentioned before, this tool provides a framework to scan the external macro-environmental factors that might impact an organization. It allows organizations to anticipate challenges and opportunities, aiding in strategic planning.
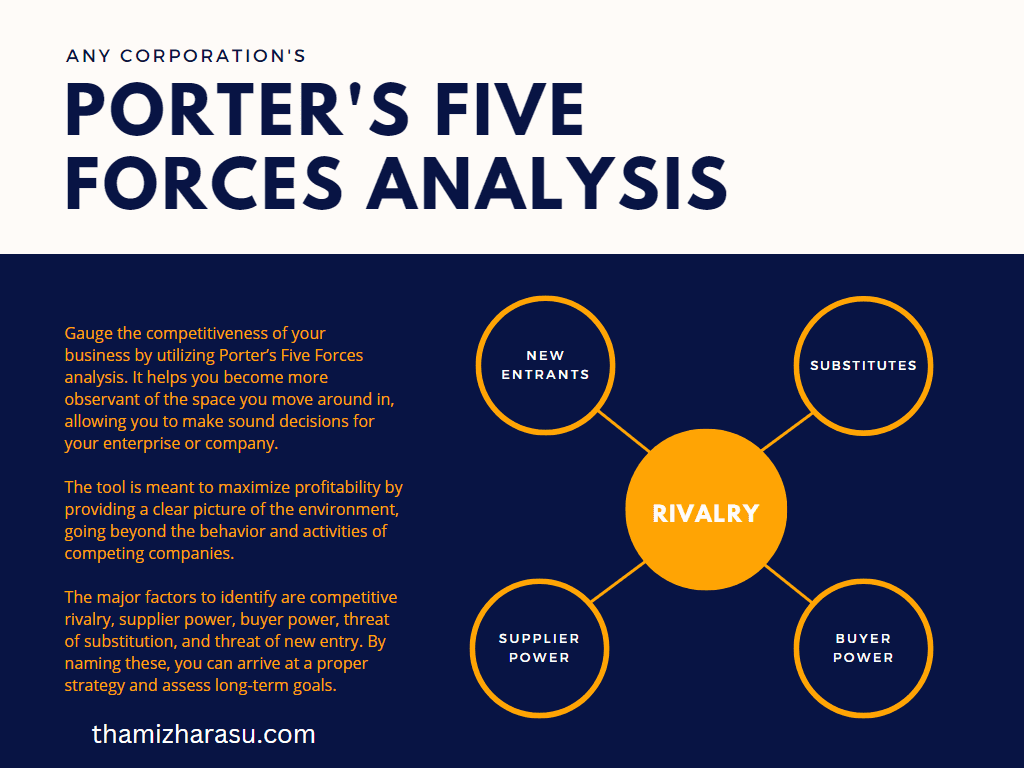
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis: This tool helps analyze the competitive environment in which a company operates. It looks at five forces: the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers, the bargaining power of suppliers, the threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of competitive rivalry.
Value Chain Analysis: Developed by Michael Porter, this tool allows businesses to break down their activities to understand their valuable contribution. This understanding can help businesses optimize and streamline these activities for maximum value creation and competitive advantage.
Each of these tools contributes to effective strategic planning and execution in its unique way. They aid in analyzing the current situation, making informed decisions, setting strategic objectives, and monitoring progress. Using these tools in combination can provide a comprehensive and insightful view of the organization’s strategic position and the business environment, leading to more robust strategic management.
6. Competitive Advantage and Strategic Management: The Connection
In today’s highly competitive business landscape, achieving a competitive advantage is crucial for any organization’s survival and success. Strategic management plays a key role in helping businesses achieve and maintain this competitive edge. Here’s how:
Understanding the Business Environment: Strategic management involves a thorough analysis of the internal and external environment, including competitors, market trends, customer behaviors, and macro-environmental factors. This deep understanding helps businesses identify opportunities they can exploit and threats they need to prepare for, giving them an edge over competitors who may not be as well-prepared.
Setting Clear Direction: Strategic management involves setting a clear vision, mission, and strategic objectives. This gives the organization a clear direction and focus, making all efforts and resources purposeful. This clear sense of direction can differentiate an organization in the marketplace.
Leveraging Strengths: A key part of strategic management is identifying and leveraging the organization’s unique strengths. Whether it’s a strong brand, innovative products, superior customer service, or efficient processes, these strengths can differentiate the organization and give it a competitive advantage.
Mitigating Weaknesses: Strategic management also involves identifying and addressing the organization’s weaknesses. By doing so, businesses can prevent competitors from exploiting these weaknesses, thus maintaining their competitive position.
Continuous Improvement: Strategic management is not a one-time process but a continuous one. It involves regularly reviewing and adjusting strategies based on changing market conditions and internal performance. This culture of continuous improvement helps businesses stay ahead of the competition.
Innovation: Strategic management encourages innovation by fostering an environment where new ideas are welcomed and explored. Innovation can lead to unique products, services, or processes that set the organization apart from its competitors.
Efficient Resource Allocation: Strategic management ensures that an organization’s resources are efficiently allocated towards activities that support its strategic objectives. This effective utilization of resources can lead to superior performance and a competitive edge.
In conclusion, strategic management is crucial in helping businesses gain a competitive advantage. By helping businesses understand their environment, set clear direction, leverage strengths, mitigate weaknesses, innovate, and use resources efficiently, strategic management gives them the tools they need to stand out in the market.
7. The Importance of Strategic Leadership in Strategic Management
Strategic leadership plays a pivotal role in the process of strategic management. It involves the ability to influence and direct an organization toward achieving its long-term goals and vision. It’s the strategic leaders who navigate the organization through the complexities of the external environment and internal dynamics to maintain a competitive edge. Here’s why strategic leadership is so critical in strategic management:
Vision Setting: Strategic leaders are responsible for setting the vision of the organization. They articulate a compelling future state that motivates employees and aligns with the organization’s strategic direction. A clear and inspiring vision is a key element of successful strategic management.
Strategy Formulation: Strategic leaders play a crucial role in formulating the organization’s strategy. They make key decisions about the strategic direction based on an understanding of the external environment and the organization’s capabilities.
Strategy Execution: A strategy is only as good as its execution. Strategic leaders ensure that strategies are effectively implemented throughout the organization. They align resources, establish strategic controls, and create processes to execute the strategy.
Change Management: Strategic leaders are often at the forefront of driving change in the organization. They anticipate, initiate, manage, and champion changes that are necessary for strategic success. This includes fostering a culture that embraces change and innovation.
Developing Others: Strategic leaders are responsible for developing future leaders who can support strategic initiatives. They create a learning environment that encourages skill development, knowledge sharing, and professional growth.
Decision Making: Strategic leaders make critical decisions that can significantly impact the organization’s strategic direction. They use their judgment and analytical skills to make informed decisions that align with the organization’s strategic objectives.
Building a Culture of Excellence: Strategic leaders play a key role in fostering a culture that values excellence, innovation, and continuous improvement. They set high standards, promote best practices, and recognize and reward exceptional performance.
In essence, strategic leadership is the linchpin of strategic management. Effective strategic leaders are not just involved in setting the strategic direction; they are instrumental in bringing it to life. They guide the organization through the strategic management process, ensure alignment between strategy and execution, and lead the organization toward its strategic objectives.
8. Case Study Analysis: Successful Strategic Management Practices
Case studies can provide valuable insights into the application of strategic management principles. They offer concrete examples of how organizations have used strategic management to navigate challenges, seize opportunities, and achieve success. Let’s look at a few examples:
Apple Inc.: Apple is renowned for its innovation, design, and branding – all of which are outcomes of effective strategic management. Apple’s vision of creating innovative and high-quality products has guided its strategic direction. The company continuously scans its external environment for technological trends and consumer preferences, enabling it to introduce ground-breaking products like the iPhone, iPad, and Apple Watch. Apple also leverages its strengths, such as its strong brand and innovative capabilities, to gain a competitive edge.
Amazon: Amazon’s strategic management practices have transformed it from an online bookstore into a global e-commerce and technology giant. Amazon’s mission to be Earth’s most customer-centric company drives its strategy. The company uses data analytics to understand customer behaviors and needs deeply, allowing it to offer personalized experiences and a vast range of products and services. Amazon is also known for its innovation, whether it’s the Kindle e-reader, Amazon Prime, or its foray into cloud computing with AWS.
Netflix: Netflix has leveraged strategic management to disrupt the entertainment industry. Recognizing the potential of streaming technology and changing consumer behaviors, Netflix pivoted from its DVD rental business to online streaming. The company also invests heavily in original content, setting it apart from competitors. Netflix uses data analytics to understand viewer preferences and habits, informing its content strategy and personalized recommendations.
Southwest Airlines: Southwest Airlines has used strategic management to become one of the most profitable airlines in the U.S. The company’s strategy focuses on providing low-cost, high-quality customer service. Southwest achieves this through efficient operations, such as using a single type of aircraft to reduce maintenance costs and a strong organizational culture that emphasizes customer service.
These case studies illustrate how strategic management can guide organizations toward success. By understanding their environment, setting clear strategic objectives, leveraging their strengths, mitigating weaknesses, and effectively implementing their strategies, these companies have managed to gain a competitive advantage and achieve their goals.
9. The Future of Strategic Management: Trends and Predictions
As we look toward the future, several emerging trends are set to shape the field of strategic management. These trends reflect the changing business landscape and the evolving needs and expectations of stakeholders. Here are a few key trends and predictions:
Sustainability and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): Sustainability and CSR are becoming integral to strategic management. Stakeholders, including customers, employees, and investors, are increasingly expecting businesses to operate responsibly and contribute positively to society and the environment. Companies are incorporating sustainability into their strategies, recognizing that sustainable practices can lead to competitive advantage, improved reputation, and long-term success.
Digital Transformation: The digital revolution is reshaping industries and altering competitive dynamics. Businesses are leveraging digital technologies to transform their operations, enhance customer experiences, and create new business models. Digital transformation is becoming a strategic priority, and organizations need to manage this transformation effectively to stay competitive.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Data Analytics: AI and data analytics are providing businesses with unprecedented insights into their operations, customers, and markets. These technologies are helping businesses make more informed strategic decisions, predict trends, personalize offerings, and improve efficiency. The strategic use of AI and data analytics will be a key differentiator in the future.
Agility and Resilience: The COVID-19 pandemic has underscored the importance of agility and resilience in strategic management. Businesses need to be able to adapt quickly to changing circumstances and bounce back from disruptions. Strategies are becoming more flexible and dynamic, with an emphasis on scenario planning, risk management, and continuous learning.
Employee Experience and Wellbeing: As the war for talent intensifies, businesses are recognizing the strategic importance of employee experience and well-being. They are creating strategies to attract, engage, and retain talent, recognizing that their people are a key source of competitive advantage.
Innovation and Creativity: As competition intensifies and the pace of change accelerates, innovation and creativity are becoming critical strategic priorities. Businesses are fostering cultures of innovation, investing in research and development, and exploring new ways of creating value for their customers.
These trends suggest that the future of strategic management will be more dynamic, data-driven, socially responsible, and people-focused. Businesses that can effectively navigate these trends and embed them into their strategic management practices will be well-positioned for success in the future.
Conclusion:
Strategic management is an essential discipline that enables organizations to navigate the complexities of the business world, seize opportunities, mitigate risks, and build a sustainable competitive advantage. It’s a continuous, dynamic process that requires understanding the environment, setting clear objectives, leveraging strengths, mitigating weaknesses, and effectively implementing strategies. As we look towards the future, trends like sustainability, digital transformation, AI, agility, and a focus on employee wellbeing are set to shape the field of strategic management. By embracing these trends and incorporating them into their strategic practices, organizations can gear up for success in the ever-evolving business landscape.
